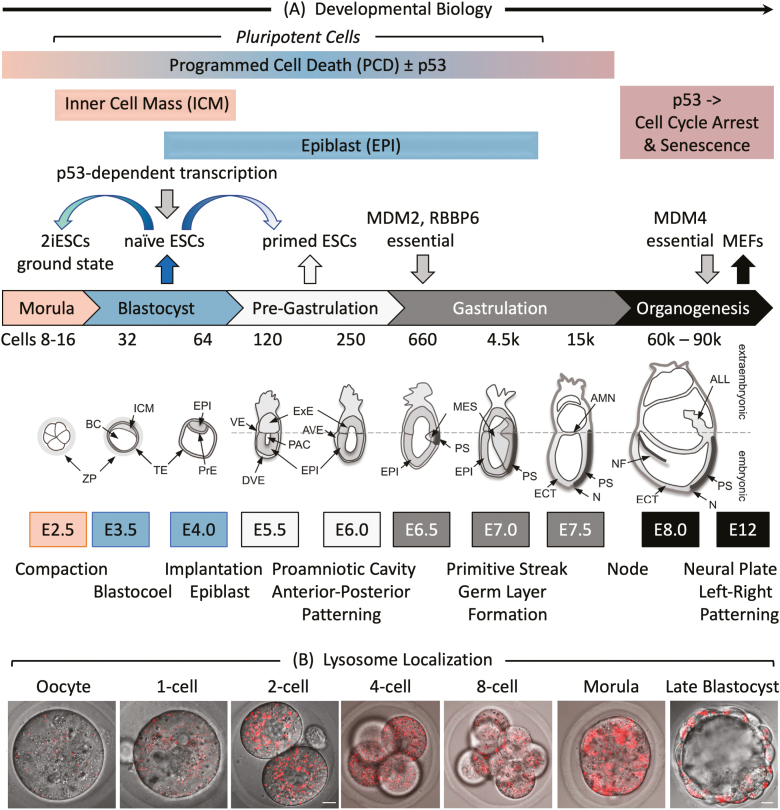
Figure 1.
Early mouse embryonic development. (A) The number of cells, days post-coitum (E2.5-E12), and morphogenetic events are indicated. ALL, allantois; AMN, amnion; AVE, anterior visceral endoderm; BC, blastocyst cavity; DVE, distal visceral endoderm; ECT, ectoderm; EPI, epiblast; ExE, extraembryonic ectoderm; ICM, inner cell mass; MES, mesoderm; N, node; NF, neural fold; PAC, proamniotic cavity; PrE, primitive endoderm; PS, primitive streak; TE, trophectoderm; VE, visceral endoderm; ZP, zona pellucida. Adapted from Ref. 116. Preimplantation development begins with totipotent blastomeres (1-8 cell stage) encapsulated by the zona pellucida. Totipotent cells can give rise to both placental and embryonic cells. When the blastomeres develop cell-to-cell adhesion (compaction), the outer blastomeres differentiate into the trophectoderm while the remaining blastomeres form the inner cell mass. The epithelial trophoblast cells (trophectoderm) are multipotent; they differentiate only into cells required for implantation and placentation. The inner cell mass (recognized upon formation of a blastocoel cavity) differentiates into the epiblast and the primitive endoderm. Postimplantation development begins when the primitive endoderm differentiates into multipotent visceral and parietal endoderm. Mesoderm and ectoderm are derived from the epiblast during gastrulation. Gastrulation begins at the primitive streak, from which mesoderm and endoderm progenitor’s ingress and begin to differentiate.117 Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) are derived from E12-E14 embryos. Ablation of the Mdm2, Rbbp6, or Mdm4 gene is lethal in embryos at the indicated times. Mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) are derived from the epiblast in blastocysts.49 mESCs cultured in the presence of serum and LIF interleukin-6 are considered “naïve” pluripotent cells, because they can give rise to all the cells of the embryo, but not to the trophectoderm. Naïve mESCs cultured in defined medium (no serum) containing 2 metabolic inhibitors are considered totipotent “ground-state” ESCs (2iESCs), because they give rise to both extraembryonic and embryonic cells. Naïve mESCs cultured in the presence of activin and fibroblast growth factor generate pluripotent “primed” ESCs, because they give rise to the same cells as “naïve mESCs,” but they cannot generate chimeric animals.118 Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and mouse epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) are derived from the epiblast of post-implantation blastocysts.48 (B) Images of LysoTracker Red stained oocytes and preimplantation embryos revealed that the number of lysosomes increased after fertilization.36 Scale bar is 10 µm.