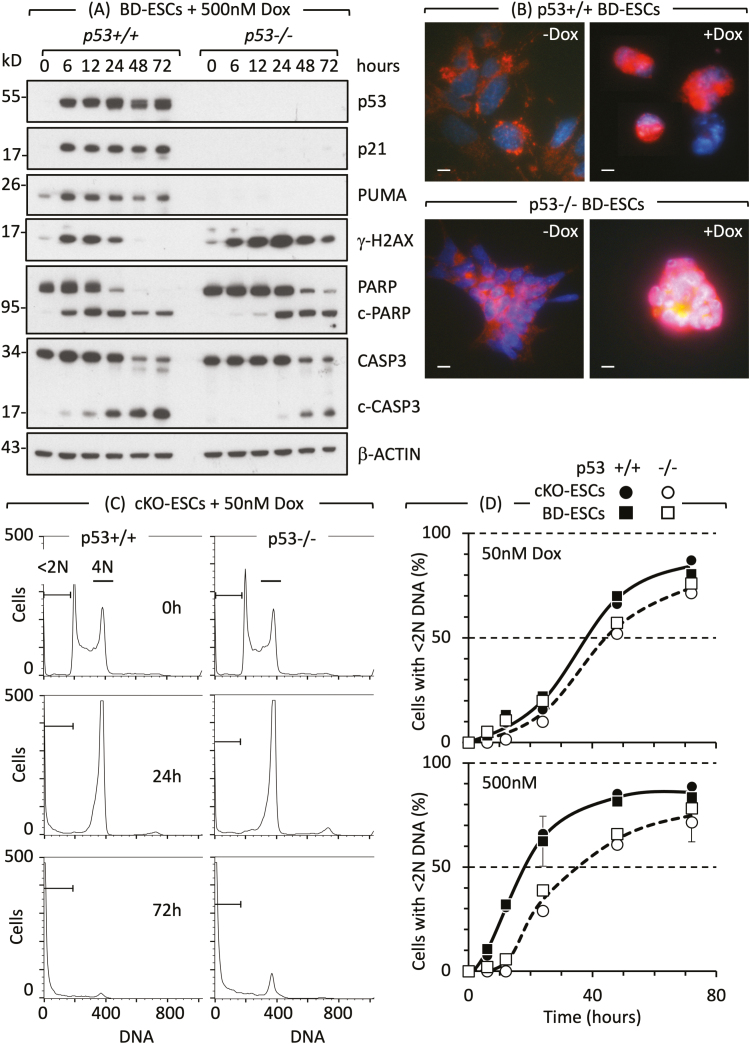
Figure 2.
Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in naïve ESCs are not dependent on p53. (A) Doxorubicin/Adriamycin (Dox) induced DNA damage (γH2AX expression), DNA damage response (PARP to c-PARP cleavage) and apoptosis (CASP3 to c-CASP3 cleavage) in ESCs derived from p53+/+ and p53−/− mouse blastocysts (BD-ESCs, “chronic phenotype”). ESCs were cultured with or without 500 nM Dox. At the times indicated, attached and unattached cells were combined, and total cellular proteins analyzed by immunoblotting. (B) PCD was detected by translocation of AIFM (red) from cytoplasm to nuclei (blue) in BD-ESCs cultured with 500 nM Dox for 16 h. Scale bar is 15 µm. (C) A transient accumulation of cells with 4N DNA content is characteristic of a DNA damage-induced G2-arrest. The G2-checkpoint was activated within 24 h and apoptosis within 72 h by 50 nM Dox in both conditional knockout p53−/− ESCs and their p53+/+ parent (cKO-ESCs, “acute phenotype”). Attached and unattached cells were combined, and their DNA content quantified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Cells with <2N DNA content (apoptotic cells) and cells with 4N DNA content (G2/M phase cells) are indicated. Equivalent results were obtained with BD-ESCs. (D) Cells with <2N DNA content were quantified as a function of time cultured with Dox and normalized to 0% at zero hours. Error bars indicate ±SEM. Panels A and B are from Fig. 3B and C in Ref. 51 and panels C and D are from Figs. 2 and S2 in Ref. 51.