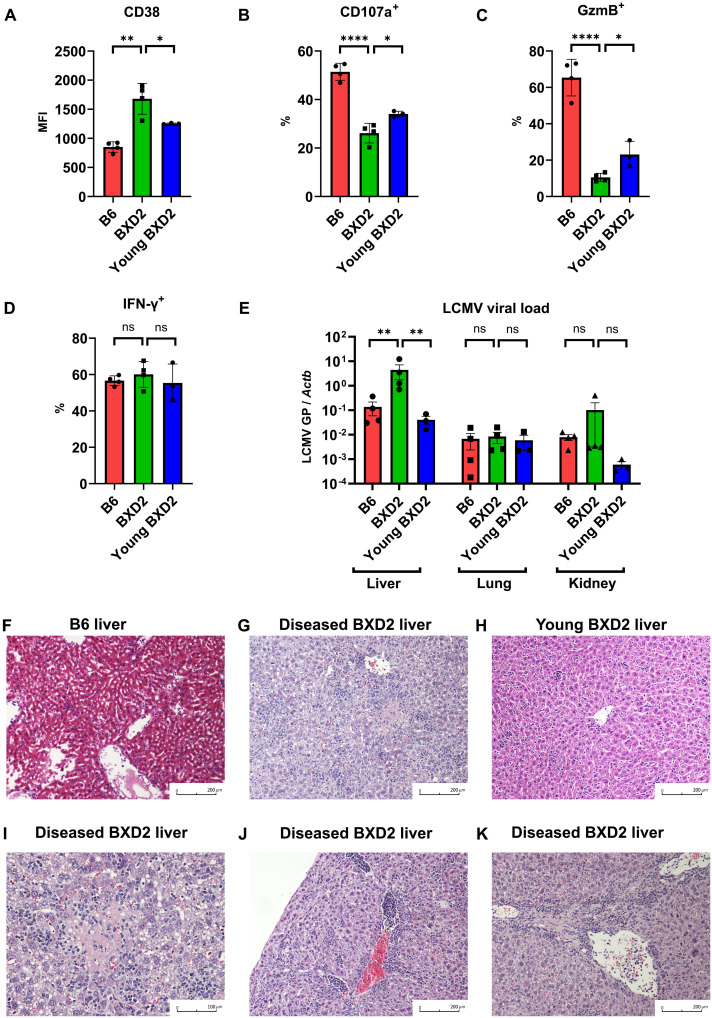
Fig. 4. Dysfunctional CD8+ T cells in BXD2 lupus mice cause viral hepatitis in LCMV infection.
(A) MFI of CD38 in gp33+ CD8+ T cells of B6, diseased BXD2, or young nondiseased BXD2 mice 8 days after LCMV Armstrong infection. (B to D) Percentage of positive cells expressing CD107a (B), granzyme B (C), and IFN-γ (D) in gp33+ CD8+ T cells of B6, diseased BXD2, or young nondiseased BXD2 mice 8 days after LCMV Armstrong infection. (E) LCMV viral load 8 days after LCMV Armstrong infection using quantitative PCR of glycoprotein gene normalized by tissue ACTB in liver, kidney, and lung of B6, diseased BXD2, or young nondiseased BXD2 mice. (F to H) Representative liver histology of B6 (F), diseased BXD2 (G), or young nondiseased BXD2 (H) mice 8 days after LCMV Armstrong infection. (I to K) Representative liver histology of diseased BXD2 mice 8 days after LCMV Armstrong infection showing focal lesion of necrosis (I) and portal and periportal inflammation (J and K). Data are means ± SD (A to D), mean ± SE (E); statistical analysis by two-tailed t test. ns = P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.