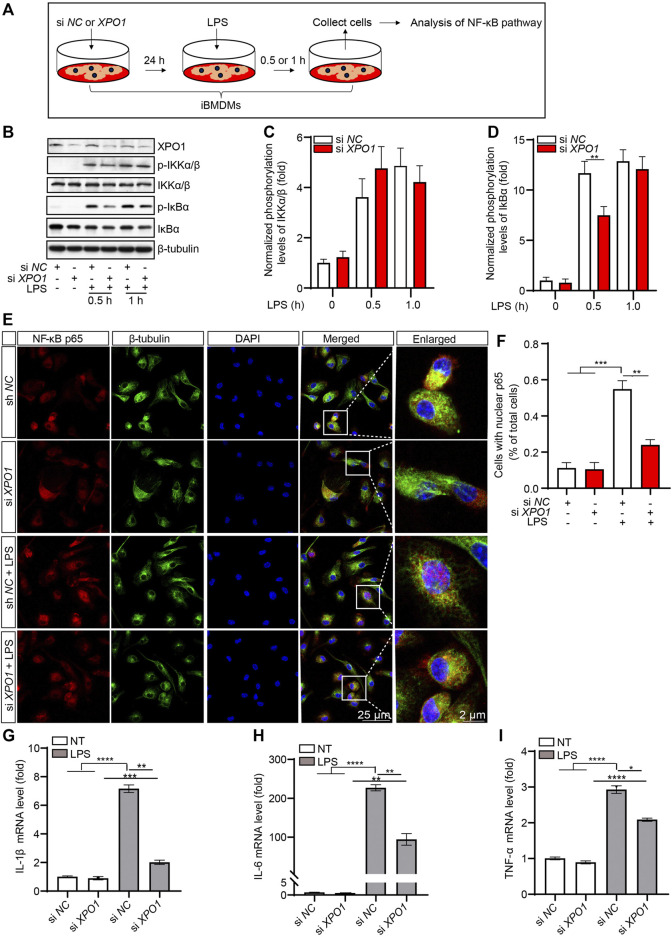
FIGURE 4.
Silencing XPO1 inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway and exerts anti-inflammatory activity. (A) iBMDMs transfected with siRNA against XPO1 or scrambled siRNA were treated with LPS for 0.5 and 1 h, respectively, and then the cell lysates were collected for analysis by Western blotting (B). The gray values of the phosphorylated and total IKKα/β (C) and IκBα (D) bands were analyzed with ImageJ. (E,F) PMs transfected with siRNA against XPO1 or scrambled siRNA were stimulated with LPS for 2 h, and then the cells were fixed and stained with a rabbit anti-NF-κB p65 antibody and mouse anti-β-tubulin antibody (E), and the number of cells containing nuclear p65 was analyzed by ImageJ (F). Scale bars, 25 μm for low-magnification images and 2 μm for high-magnification images, respectively. (G–I) iBMDMs transfected with siRNA against XPO1 or scrambled siRNA were treated with LPS for 6 h, and then the mRNA levels of IL-1β (G), IL-6 (H), and TNF-α (I) were detected by real-time PCR. (* indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, *** indicates p < 0.001, **** indicates p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA).