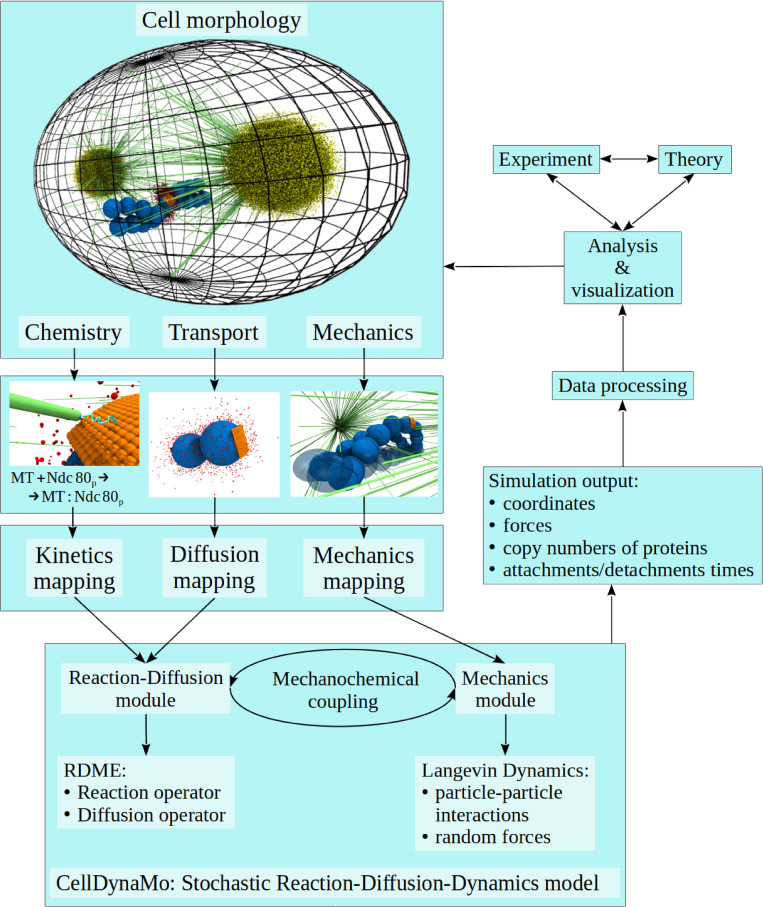
Fig 3. Design of Stochastic Reaction-Diffusion-Dynamics model-based implementation of CellDynaMo package.
CellDynaMo requires the initial input (reaction rate constants, copy numbers of biomolecules), the force field parameters (stretching and bending rigidities, KT-MT attachment strength), and cell morphology (number of chromosomes or kinetochore pairs, membrane shape). These specify cell morphology and geometry of spatial arrangements of different cell components (Fig 1), biochemical kinetics (Tables 2, 3 and 4), molecular transport (Table 3), and force-generating properties (Table 1). A list of parameters used in CellDynaMo package is provided in Table A in S1 Text. The RDME is solved numerically for all subcells at each time point. When changes to the mechanical state occur, the RDME switches off and the LD switches on. When a new state of mechanical equilibrium is reached, CellDynaMo writes an output for a particular time point, which includes coordinate file, force file, and file with subcell specific content. These can then be used to analyze and visualize the simulation data, and to compare with experiments and with theoretical predictions.