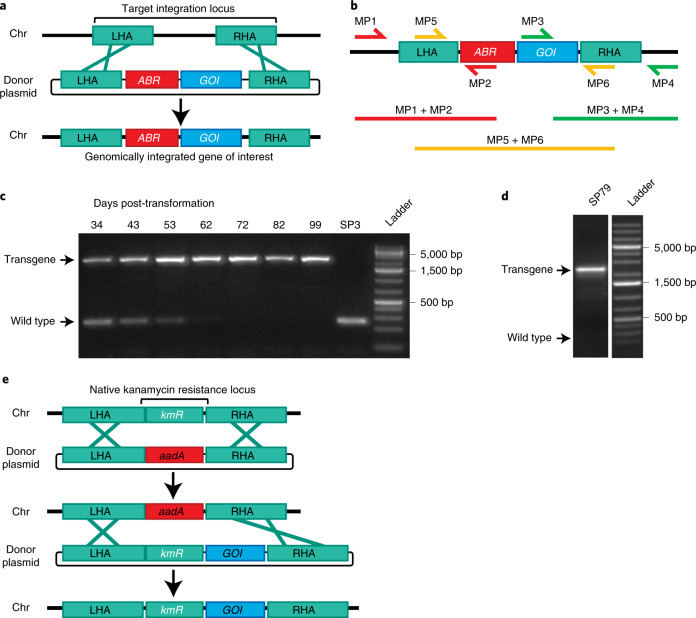
Fig. 1. Homologous recombination into the spirulina chromosome.
a, Plasmid DNA containing an antibiotic-resistance (ABR) gene and a gene of interest (GOI) flanked by LHA and RHA. A double-crossover inserts ABR and GOI into the target locus, replacing genomic DNA. b, Diagram of primer pairs for PCR genotyping. Amplification of LHA and RHA includes one priming site (MP1 and MP4) present only in the spirulina genome at the target locus. Sanger sequencing of the PCR product of the central primer pair (MP5 + MP6) confirmed faithful integration. c, Segregation analysis of strain SP607. Spirulina strain SP3 was transformed on day 0 with donor DNA containing an antibiotic marker and a transgene and cultured under antibiotic selection. Spirulina was collected at the indicated time points, and full transgene products (MP5 + MP6) were amplified from genomic DNA by PCR. Genotyping was performed once. d, Long-term transgene stability. Spirulina strain SP79 was genotyped after continuous culture for >3 years. PCR from genomic DNA was performed with primers targeting the full transgene region (MP5 + MP6). Genotyping was performed once. e, Strategy of markerless transgene integration (see main text for details).