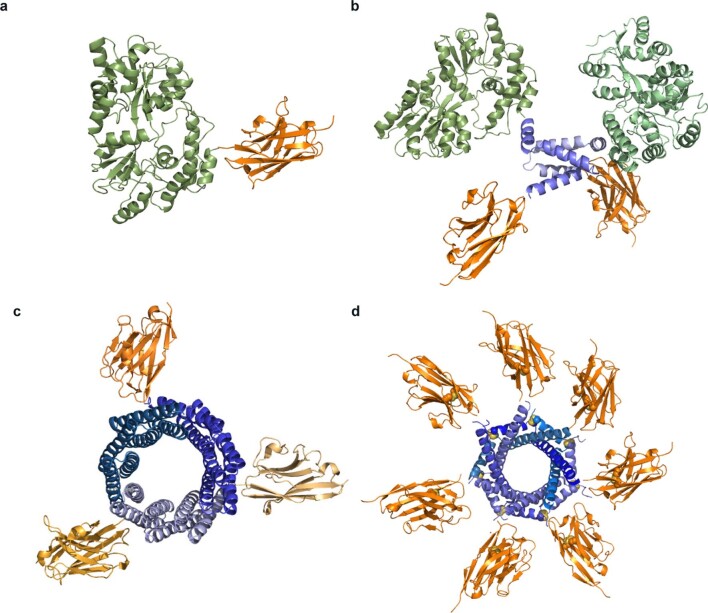
Extended Data Fig. 4. Model representations of heterologous proteins designed for expression in spirulina.
a. Ribbon representation of a monomeric VHH (orange; PDB ID:6WAQ)54 with the solubility enhancer, MBP (green; PDB ID: 5M13)55. The mature, folded protein results in a monomeric VHH as a fusion to MBP and a C-termini 6X-his affinity tag. b. Ribbon representation of a VHH (orange) with a dimerization motif (blue; PDB ID: 5HVZ)56 and the solubility enhancer, MBP (green). The mature, folded protein results in a dimeric VHH where dimerization is facilitated by the disulfide-linked dimerization motif. The single polypeptide also contains the solubility enhancer MBP and C-terminal 6X-his affinity tag. c. Ribbon representation of a trimeric VHH (orange). The mature, folded protein results in trimeric VHH (orange) where trimerization is facilitated by the self-assembling homotrimer t-cTRP9X3 (blue)57. The single polypeptide also contains a C-terminal 6X-his affinity tag. d. Ribbon representation of heptameric VHH (orange) with the heptamerization motif (blue; PDB ID: 4B0F)58. The mature, folded protein results in a heptameric VHH where heptamerization is due to intrachain disulfide bond between individual protomers. The polypeptide also contains an N-terminal solubility enhancer MBP fusion and C-terminal 6X-his affinity tag. All structures generated using Pymol (Schrodinger).