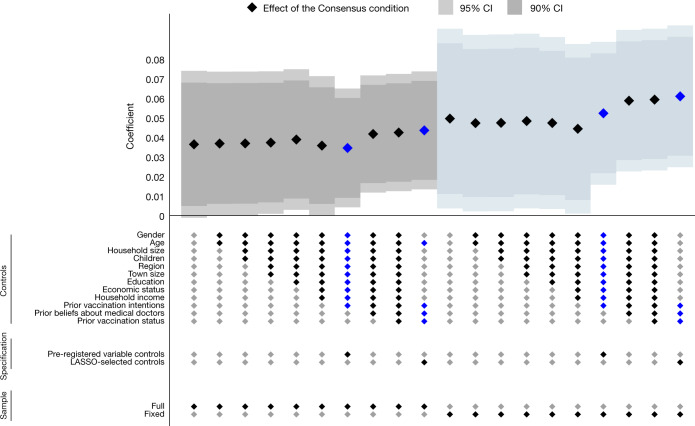
Fig. 5. Effects of the Consensus condition on vaccine uptake: robustness.
A sample of the adult Czech population. This specification chart plots the estimated effects of Consensus on the likelihood of vaccine uptake for a pooled sample across waves 6–11 (when the vaccine was available for all adults). All specifications include wave fixed effects. Markers show the estimated effects, the darker or lighter whiskers denote the 90% or 95% confidence interval, respectively, based on standard errors clustered at the respondent level. No adjustments were made for multiple comparisons. We report a range of linear probability model specifications by sequentially adding sets of control variables in Extended Data Table 1. The main specifications are marked by blue diamonds. We report all specifications for both the full sample (left-hand side) and the fixed sample (right-hand side). Full sample: Consensus condition n = 5,145 (981 clusters = respondents); Control n = 5,137 (983 clusters = respondents). Fixed sample: Consensus n = 3,684 (614 clusters = respondents); Control n = 3,588 (598 clusters = respondents). Extended Data Table 4 shows the regression results in detail.