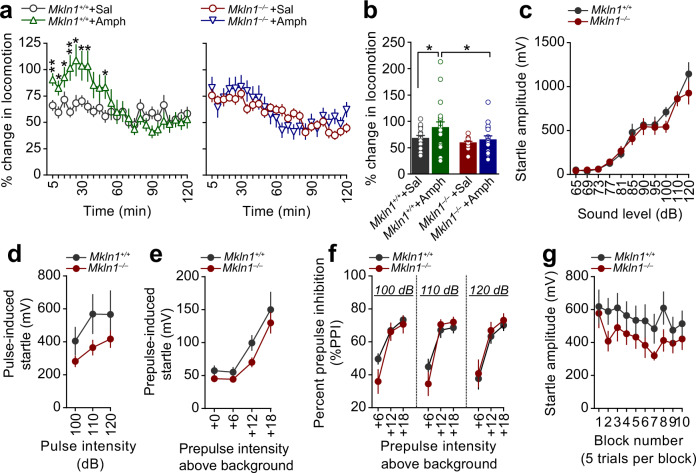
Fig. 2. Mkln1-null mice exhibit intact sensorimotor gating function but decreased locomotor sensitivity to amphetamine.
a Locomotor response to acute amphetamine (2.5 mg/kg) challenge after considering differences in baseline locomotion. Compared with the respective saline-treated groups, amphetamine significantly increased locomotor activity in Mkln1+/+ mice (left panel) but had negligible effect in Mkln1–/– mice (right panel; genotype × drug × time bins: (F(23,1518) = 2.23, P < 0.01). Restricted analyses to each genotype groups revealed a pronounced drug effect in Mkln1+/+ mice (drug × time bins: F(23,782) = 3.20, P < 0.0001) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test for pairwise comparisons (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) but not in the Mkln1–/– group. b Overall, Mkln1–/– mice showed significantly diminished locomotor response to amphetamine compared with Mkln1+/+ controls (genotype: F(1,66) = 5.47, P < 0.05) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test for pairwise comparisons (*P < 0.05). c Both Mkln1–/– and Mkln1+/+ mouse groups show a comparable increase in startle reactivity in response to pulse stimuli of increasing sound intensity (dB intensity: F(9,144) = 65.82, P < 0.0001). d, e The absence of muskelin did not affect startle response to pulse-alone (d) and prepulse-alone (e) stimuli. f Percent PPI depicted as function of increasing prepulse intensities for each pulse intensity (prepulse intensities: +6, +12, and +18 dB above background (65 dB) noise). Mkln1–/– mice show highly similar PPI levels as Mkln1+/+ controls (prepulse: F(2,52) = 149.17, P < 0.0001). g Habituation of startle responses following the presentation of 120 dB acoustic stimuli. Each block comprises 5 trials of acoustic stimuli. Both genotypes show a decline in the response amplitude as a function of trials (trial: F(9,153) = 3.14, P < 0.01). For data related to a, b (Amph: Mkln1+/+ (N = 21: M = 10, F = 11); Mkln1–/– (N = 18: M = 7, F = 11); Saline: Mkln1+/+ (N = 17: M = 8, F = 9); Mkln1–/– (N = 18: M = 8, F = 10); c (Mkln1+/+ (N = 10: M = 5, F = 5); Mkln1–/– (N = 10: M = 5, F = 5); d–f (Mkln1+/+ (N = 15: M = 8, F = 7); Mkln1–/– (N = 15: M = 8, F = 7); g (Mkln1+/+ (N = 11: M = 5, F = 6); Mkln1–/– (N = 10: M = 5, F = 5). Data are presented as means ± SEM.