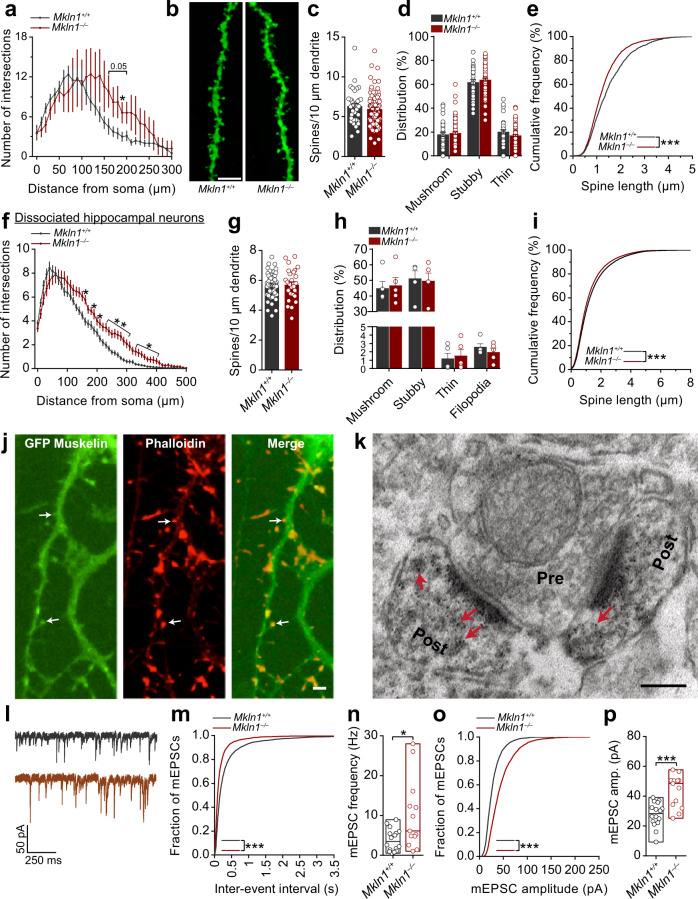
Fig. 5. Mkln1 deletion alters neuronal morphology and enhances AMPAR-mediated synaptic transmission.
a Sholl analysis of the dendritic tree architecture revealed a strong trend for increased dendrite complexity in CA1 pyramidal neurons of Mkln1–/– mice (genotype × radius: F(30,330) = 1.65, P < 0.05 followed by Bonferroni post hoc test for pairwise comparisons (P = 0.05, *P < 0.05). Mkln1+/+ (n = 8 neurons) and Mkln1–/– (n = 5 neurons). b Representative images of DIL dye staining of a dendrite segment and spines from Mkln1–/– and Mkln1+/+ CA1 pyramidal neurons. Scale bar = 5 µm. c Graphical depiction of comparable spine density in apical branches from Mkln1–/– and Mkln1+/+ CA1 pyramidal neurons (genotype: β = −0.29, t = −0.72, P = 0.47). d Spine type distribution on apical branches was identical for Mkln1–/– and Mkln1+/+ CA1 pyramidal neurons. Mkln1+/+ (n = 11 neurons, 37 dendrites), Mkln1–/– (n = 35 neurons, 86 dendrites). The mixed model analysis accounts for non-independence in the data from multiple dendrites per neuron. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. e Spine lengths of all analyzed spines plotted as a cumulative frequency, which reveals a significant shift towards shorter spine lengths in Mkln1–/– CA1 pyramidal neurons (two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) test: D = 0.126, P < 0.0001). Mkln1+/+ (n = 66 dendrites, 2202 spines), Mkln1–/– (n = 146 dendrites, 4592 spines). Data (a–e) are derived from three mice per genotype. f Sholl analysis of the dendritic arbor shows that Mkln1 deletion significantly increases dendritic branching in dissociated hippocampal neurons (Genotype: F(1,19) = 8.53, P < 0.01); genotype × radius: F(49,931) = 2.67, P < 0.0001) followed by Bonferroni post hoc test for pairwise comparisons (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Mkln1+/+ (116 neurons from n = 12 embryos) and Mkln1–/– (90 neurons from n = 9 embryos). Analysis treating each embryo (instead of each neuron) as an independent sample. Spine density (g) and ratio of spine types (h) was comparable between Mkln1+/+ and Mkln1–/– cultured hippocampal neurons (Genotype: β = −0.03, t = −0.12, P = 0.9). Mkln1+/+ (n = 55 neurons) and Mkln1–/– (n = 28 neurons). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. i The cumulative frequency distribution of spine length shows a significant leftward shift (shorter spines) for Mkln1+/+ spines (two-sample KS test: D = 0.049, P < 0.0001). Mkln1+/+: (n = 55 neurons, 73,422 spines), Mkln1–/–: (n = 28 neurons, 39733 spines). Data (f–i) are derived from 5 independent preparations. j Cultured hippocampal neurons expressing GFP-tagged muskelin (green: left panel) and incubated with fluorochrome-labeled phalloidin (red: middle panel). Arrowheads in the merged right panel point to muskelin localization in a subset of actin-rich dendritic protrusions. Scale bar, 5 µm. k Electron micrograph showing immunogold labeling of mouse hippocampal ultrasections with antibodies against muskelin. Muskelin signals are detected in dendritic spines (Post, arrowheads) opposite an axon terminal (Pre). Scale bar, 150 nm. l–p Mkln1 deletion leads to enhanced AMPAR-mediated excitatory synaptic transmission. l Sample traces from whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings with downward deflections indicating AMPA-mediated mEPSCs in Mkln1+/+ (top) and Mkln1–/– (bottom) neurons. m Cumulative probability plots showing shorter interevent intervals in Mkln1–/– neurons (two-sample KS test: D = 0.23, P < 0.0001). n AMPA-mEPSC burst frequency was significantly increased in Mkln1–/– neurons (Mann–Whitney U test: U = 56.5, P < 0.05). o Cumulative distribution plot reveals a significant shift towards larger mEPSC amplitudes in Mkln1–/– neurons (two-sample KS test: D = 0.33, P < 0.0001). p Graphical representation of mean mEPSC amplitudes per neuron, which were significantly increased in Mkln1–/– neurons (Mann–Whitney U test: U = 29, P < 0.0001). Floating bars represent the min-to-max values. Scatter plots depict results per neuron, and the line within bar graphs corresponds to the group median value. Mkln1+/+ (n = 16 neurons); Mkln1–/– (n = 13 neurons) from three independent preparations.