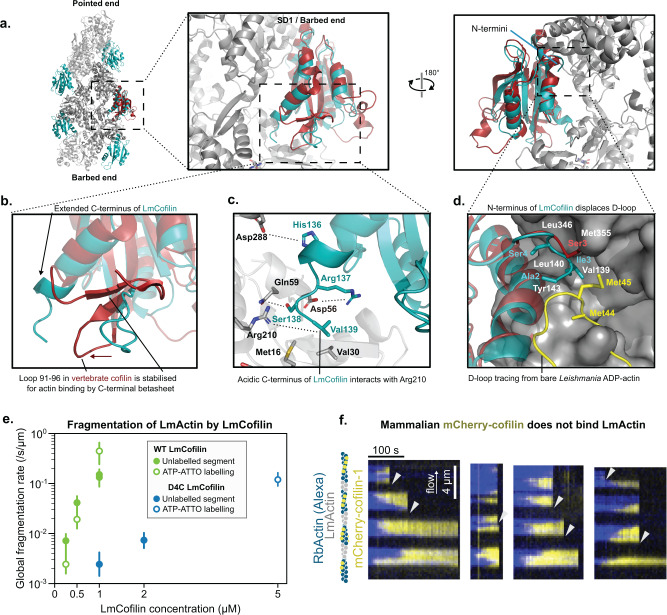
Fig. 6. Structural basis of Leishmania actin filament severing.
a Structure of the LmActin filament decorated with Leishmania cofilin. In comparison to vertebrate cofilin (in red), the Leishmania cofilin (in cyan) contains an extended C-terminal α-helix. b A close view of the C-terminal region of cofilin. In vertebrate cofilin, C-terminus forms a turn followed by a two-strand β-sheet, which stabilizes loop 91–96 to closer contact with the actin filament. This β-sheet is absent from Leishmania cofilin, which contains an extended C-terminal α-helix. c Amino acid contacts between the C-terminus of Leishmania cofilin and LmActin. The acidic C-terminus can form an ion pair with Arg210 in actin, and local hydrophobic contacts through Val139 to Met16 and Val30. His136 and Arg137 can form ion bonds to Asp288 and Asp56, respectively, in actin. d The N-terminus of Leishmania cofilin interacts with the barbed end of actin. In the cofilin-bound actin, the D-loop is unstructured (not shown in the figure), whereas in bare actin filaments the D-loop (shown in yellow) associates with the hydrophobic pocket (residues named in white) of the adjacent actin subunit. Hydrophobic Ile2 from Leishmania cofilin collides with Met45 of D-loop, and is thus expected to replace the D-loop from the hydrophobic pocket. In vertebrate cofilin (cyan), the N-terminal tracing of the structure terminates to Ser3. e Global severing rates of wild-type Leishmania cofilin (data from Fig. 5b) and a mutant Leishmania cofilin lacking the four C-terminal amino acids (D4C). Each data point was calculated by fitting the survival fraction of >60 F-actin segments (n) with a single exponential and normalized by the mean segment length (units: /s/µm, see Methods). Error bars were calculated by fitting the upper and lower values of the 95% confidence interval. For unlabeled segments with wild-type LmCofilin: 0.25 µM N = 1, n = 90; 0.5 µM N = 1, n = 90; 1 µM N = 2, n = 90, 90. For ATP-ATTO labeled segments with wild-type LmCofilin: 0.25 µM N = 1, n = 20; 0.5 µM N = 1, n = 20; 1 µM, N = 1, n = 20. For unlabeled segments with D4C LmCofilin: 1 µM N = 1, n = 90; 2 µM N = 1, n = 240. For ATP-ATTO labeled segments with D4C LmCofilin: 5 µM N = 1, n = 60. f Decoration and fragmentation of segmented filaments (Alexa-RbActin segments in blue, and unlabeled LmActin segments) by 200 nM vertebrate mCherry-cofilin-1 (yellow) from a single experiment. No decoration by mCherry-cofilin-1 is observed on unlabeled LmActin segments. The severing of filaments appears to occur mainly at the interface between LmActin and rabbit actin segments (arrowheads).