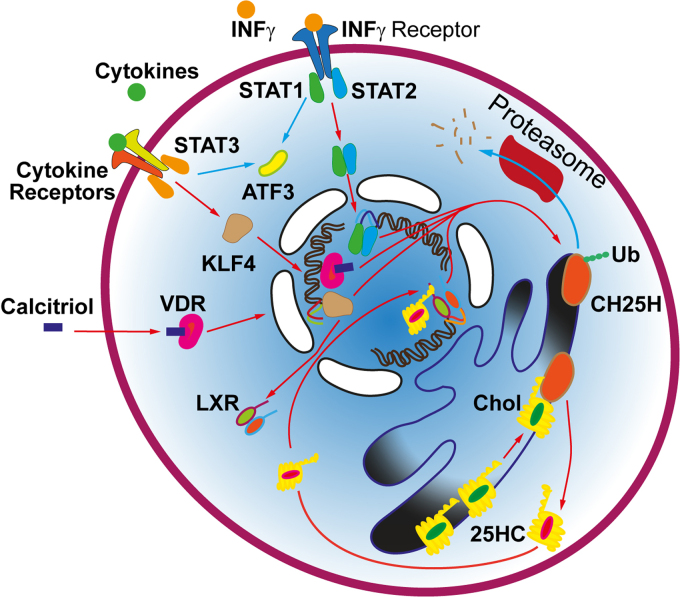
Fig. 1.
Regulation of CH25H expression. IFNγ (or INFγ) and a number of cytokines upregulate CH25H expression via stimulation of the STAT and KLF4 transcription factors [13, 16] or suppress it through the activation of ATF3 [17]. CH25H expression is activated by the stimulation of vitamin D receptors (VDRs) and liver X receptors (LXRs) [18, 19]. 25-HC is a potent ligand of the latter receptors), which creates a positive feedback between the expression of CH25H and production of 25-HC. The synthesis of 25-HC increases with increasing cholesterol levels in the ER. On the contrary, CH25H ubiquitination directs it to proteasomal degradation, resulting in the decrease in the 25-HC synthesis [20]. Blue and red arrows show negative and positive regulation of 25-HC levels, respectively.