FIGURE 2.
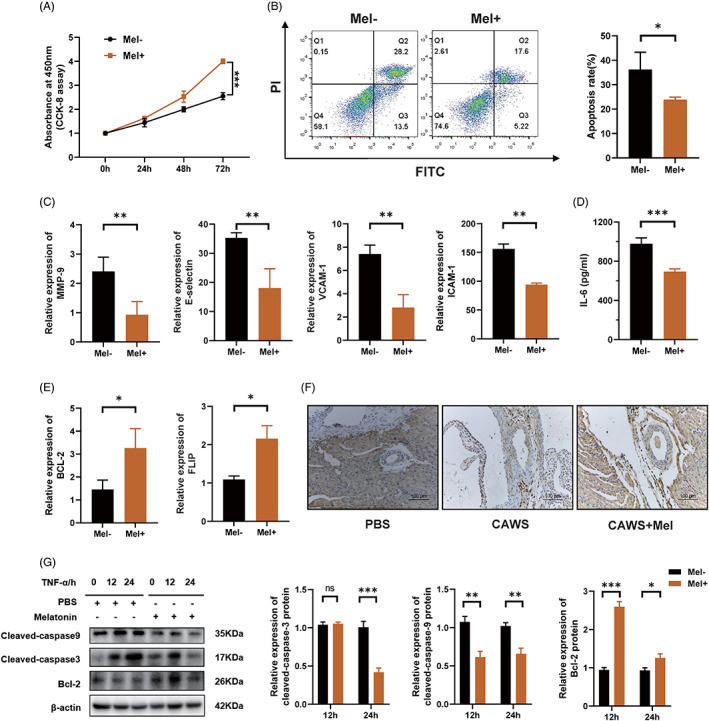
Melatonin inhibits vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. (A) Cell proliferation of HCAECs, as assessed using CCK‐8 assay; the Mel+ group received 0.5 mM melatonin pre‐treatment for 6 h, while the Mel‐ group did not. (B) After pre‐treatment with or without 0.5 mM melatonin for 6 h, the HCAECs were cultured in ECM with H2O2, to induce cell apoptosis, following which apoptosis was analysed by means of Annexin V‐FITC/PI double‐staining and flow cytometry. (C) Mel+ group was pre‐treated with 0.5 mM melatonin for 6 h, following which both the groups were stimulated with 20 ng/ml TNF‐α for 12 h and relative mRNA expression levels of endothelial cell damage markers, including MMP‐9, E‐selectin, ICAM‐1, and VCAM‐1 were detected using RT‐qPCR. (D) ELISA assay of the protein level of IL‐6 in cell culture supernatants of HCAECs. (E) The Mel+ group was pre‐treated with 0.5 mM melatonin for 6 h, following which both the groups were stimulated with 20 ng/ml TNF‐α for 12 h and relative mRNA expression levels of anti‐apoptotic genes Bcl2 and FLIP were detected using RT‐qPCR. (F) Immunohistochemical staining of anti‐apoptotic protein Bcl‐2 in mice coronary arteries. Scale bar: 100 μm. (G) The levels of Bcl‐2, cleaved‐caspase‐3, and cleaved‐caspase‐9 in HCAECs stimulated with TNF‐α, with or without melatonin pre‐treatment, were quantified using western blot. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant. Bcl‐2, B‐cell lymphoma‐2; CCK, cell counting kit; ECM, endothelial cell medium; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; HCAEC, human coronary artery endothelial cell; ICAM‐1, intercellular cell adhesion molecule‐1; Mel, melatonin; MMP‐9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; PI, propidium iodide; PLIP, FLICE inhibitory protein; TNF‐α, tumour necrosis alpha; VCAM‐1, vascular cell adhesion molecule‐1
