FIGURE 6.
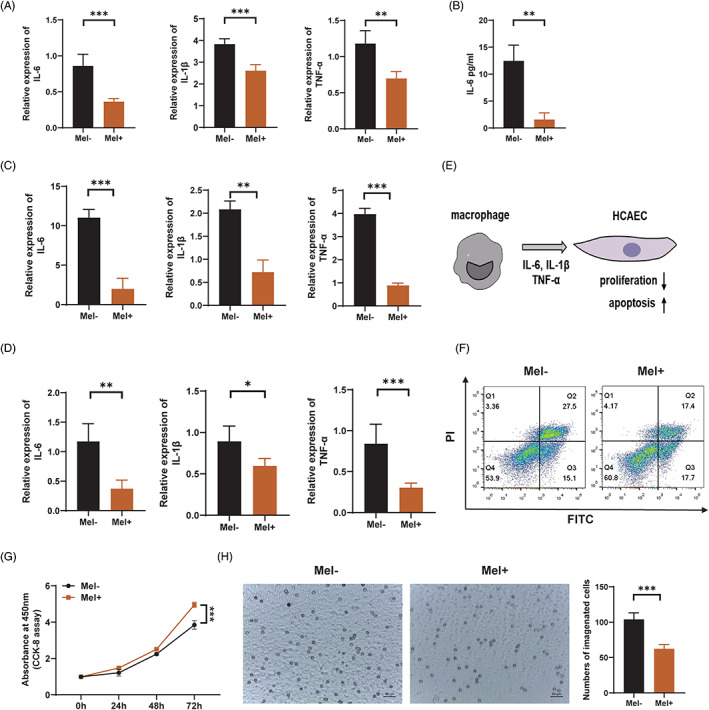
Melatonin inhibits macrophage‐mediated immunopathological damage of vascular endothelial cells in patients with Kawasaki disease. (A) Relative expression of IL‐6, IL‐1β, and TNF‐α in LPS (100 ng/ml)‐stimulated THP1 cells, with or without melatonin (0.5 mM) pre‐treatment, as detected using RT‐qPCR. (B) ELISA analysis showing the protein level of IL‐6 in the cell culture supernatant of THP1 cells treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) and melatonin (0.5 mM). (C) Relative expression of IL‐6, IL‐1β, and TNF‐α in TNF‐α (20 ng/ml)‐stimulated macrophages, as detected using RT‐qPCR. (D) Relative expression of IL‐6, IL‐1β, and TNF‐α in PBMC‐derived macrophages of KD patients, with or without melatonin (0.5 mM) pre‐treatment. (E) An in vitro co‐culture system of HCAECs and macrophages. (F) Apoptosis of HCAECs co‐cultured with macrophages, as assessed using Annexin V‐FITC/PI double‐staining and flow cytometry. (G) Cell proliferation of HCAECs co‐cultured with macrophages, as assessed using CCK8 assay. (H) Microscopic images showing the number of THP1‐derived macrophages migrating to TNF‐α‐stimulated HCAECs, as detected using transwell assay. Scale bar: 50 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant. IL‐1β, interleukin‐1 beta; IL‐6, interleukin‐6; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; TNF‐α, tumour necrosis factor alpha
