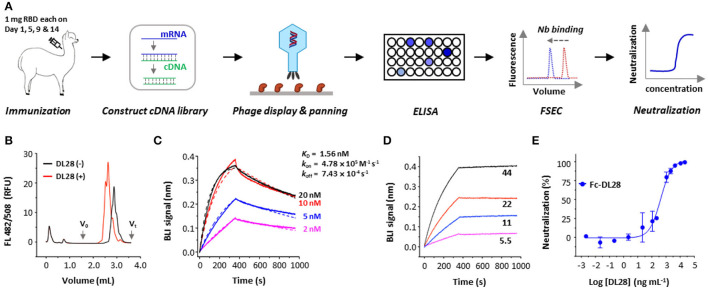
Figure 1.
Strategy and isolation of neutralizing nanobodies. (A) Schematic flowchart for the identification of neutralizing nanobodies (Nbs). Immunization dose and schedule are indicated. The mRNA was isolated from an alpaca that was immunized with the RBD. A phage display library expressing nanobodies was selected against RBD. Positive clones were screened using ELISA and fluorescence-detector size exclusion chromatography (FSEC) for RBD-binding, and purified nanobodies were screened using neutralization assays with SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses. (B) Unpurified DL28 causes earlier elution of the fluorescently labeled RBD on analytic gel filtration. (C) Binding kinetics of DL28 to RBD using BLI with RBD immobilized and DL28 as analyte at indicated concentrations (nM). Solid lines indicate original data and dotted lines indicate fitted curves. (D) Evidence for the binding between DL28 and S protein. Apparent binding kinetics are not fitted due to the existence of bridged complexes between immobilized DL28 and the trimeric analyte S. (E) Neutralization assay of Fc-DL28 against SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses.