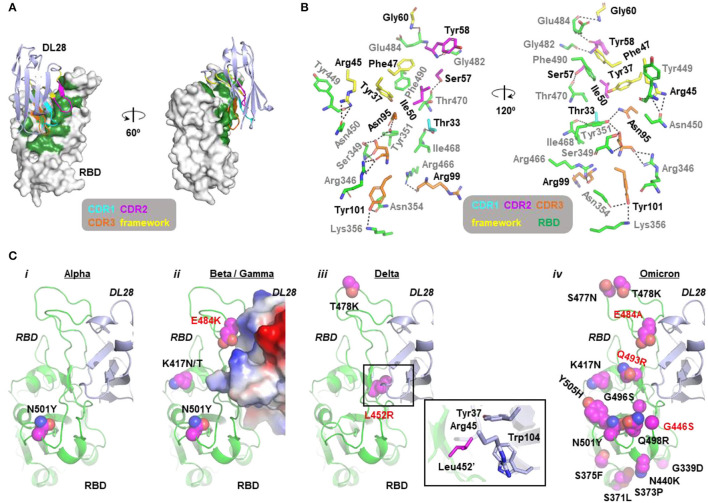
Figure 3.
Molecular insights into the activity of DL28 against SARS-CoV-2 variants. (A) The overall structure of DL28 (light blue) in complex with RBD (white). DL28 binds the high-chair-shaped RBD at one side. The binding interface is colored green. Three complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) and the framework residues involved in the binding are color-coded as indicated. (B) Stick representation of the interaction residues from DL28 (cyan, magenta, orange, and yellow) and RBD (green). DL28 residues are labeled in black and RBD residues are labeled in gray. Dash lines indicate distances within 3.8 Å. (C) The distribution of RBD mutations (magenta sphere) from the Alpha (i), Beta/Gamma (ii), Delta (iii), and Omicron (iv) variants in the context of the DL28 epitope. RBD (green) and DL28 (blue) are shown as ribbon representations except that DL28 is shown as Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver electrostatic potential surfaces in ii. The expanded view in iii highlights the interaction between Leu452' and indicated DL28 residues.