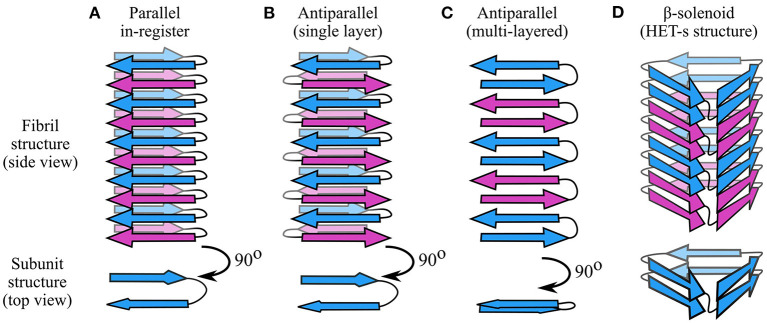
Figure 3.
Types of cross-β structures. (A) In parallel in-register structures, each subunit contributes a single strand per intermolecular β-sheet, and the strands are oriented parallel and in-register with one another. Thus, the hairpin-like structure shown in this figure has two intermolecular β-sheets. (B) In single-layered antiparallel cross-β structures, each subunit contributes a single β-strand per β-sheet, but the strand direction alternates. (C) In multi-layered antiparallel structures, each subunit contributes more than one strand per β-sheet. (D) In β-solenoids such as HET-s (Wasmer et al., 2008), subunits occupy more than one layer by coiling in a solenoidal fashion. In these schematics, adjacent subunits are alternately colored blue and purple. Each monomeric subunit in the parallel in-register and antiparallel structures is a two-strand hairpin, differing only in orientation of the strands; a different monomer structure is used for the β-solenoid, based on a simplification of the HET-s structure (Wasmer et al., 2008).