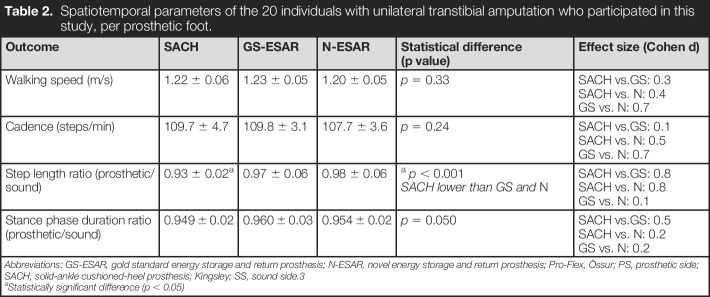
Table 2.
Spatiotemporal parameters of the 20 individuals with unilateral transtibial amputation who participated in this study, per prosthetic foot.
| Outcome | SACH | GS-ESAR | N-ESAR | Statistical difference (p value) | Effect size (Cohen d) |
| Walking speed (m/s) | 1.22 ± 0.06 | 1.23 ± 0.05 | 1.20 ± 0.05 | p = 0.33 | SACH vs.GS: 0.3 SACH vs. N: 0.4 GS vs. N: 0.7 |
| Cadence (steps/min) | 109.7 ± 4.7 | 109.8 ± 3.1 | 107.7 ± 3.6 | p = 0.24 | SACH vs.GS: 0.1 SACH vs. N: 0.5 GS vs. N: 0.7 |
| Step length ratio (prosthetic/sound) | 0.93 ± 0.02a | 0.97 ± 0.06 | 0.98 ± 0.06 |
a
p < 0.001 SACH lower than GS and N |
SACH vs.GS: 0.8 SACH vs. N: 0.8 GS vs. N: 0.1 |
| Stance phase duration ratio (prosthetic/sound) | 0.949 ± 0.02 | 0.960 ± 0.03 | 0.954 ± 0.02 | p = 0.050 | SACH vs.GS: 0.5 SACH vs. N: 0.2 GS vs. N: 0.2 |
Abbreviations: GS-ESAR, gold standard energy storage and return prosthesis; N-ESAR, novel energy storage and return prosthesis; Pro-Flex, Össur; PS, prosthetic side; SACH, solid-ankle cushioned-heel prosthesis; Kingsley; SS, sound side.3
Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05)