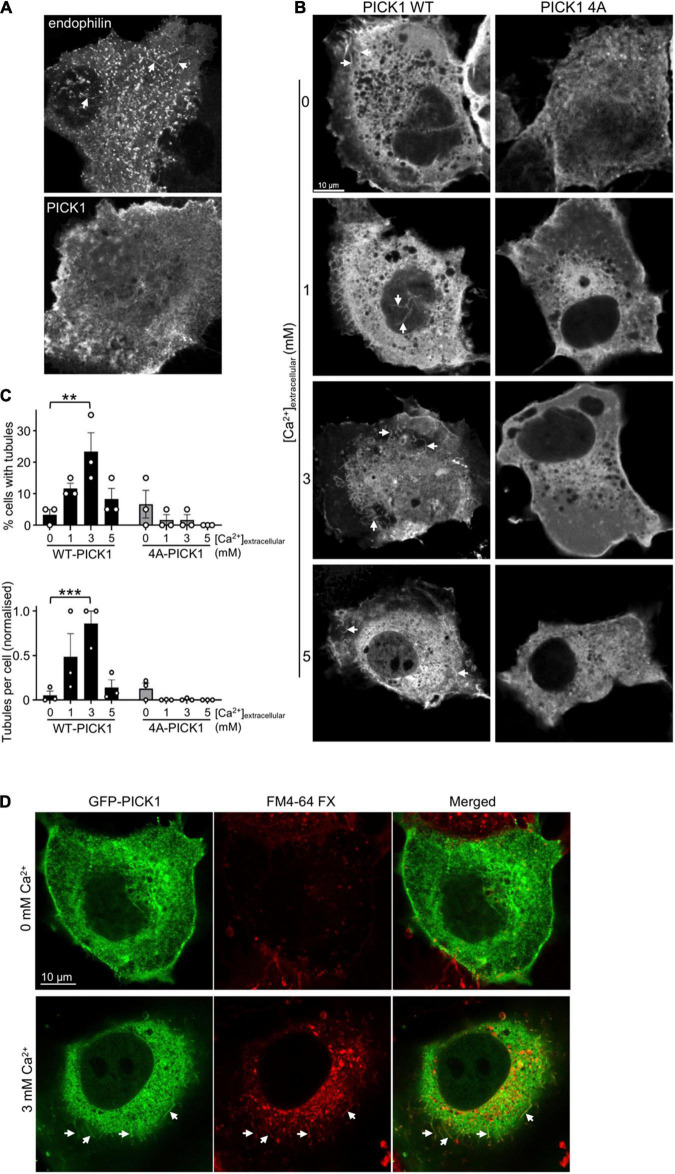
FIGURE 3.
Ca2+ stimulates cellular membrane tubulation via PICK1 dimerization. (A) COS7 cells expressing GFPPICK1 or GFPendophilin were fixed and analyzed by confocal microscopy. GFP-positive tubular structures are detectable in cells expressing GFP-endophilin (arrowheads), but not in cells expressing GFPPICK1. (B) COS7 cells expressing GFPWT-PICK1 or GFP4A-PICK1 were incubated in 0, 1, 3, or 5 mM extracellular Ca2+ and 3 μM ionomycin for 15 min prior to fixation and confocal microscopy. Arrows show tubular structures. (C) Quantification of the experiment is shown in B. Tubulation was analyzed as described in the “Materials and methods” section; 20 cells were analyzed per condition in each of three independent experiments. The top graph shows the percentage of cells with detectable tubules, and the bottom graph shows the mean number of tubules per cell. N = 3, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (D) GFPPICK1 tubules originate from the plasma membrane. Cells were treated as in B, with the lipophilic dye FM4-64FX added at the same time as ionomycin. Confocal microscopy demonstrates the colocalization of GFPPICK1 with FM4-64FX. Arrows show tubular structures.