Figure 3. Application of mouse models to identify the biological sex components for a trait of interest.
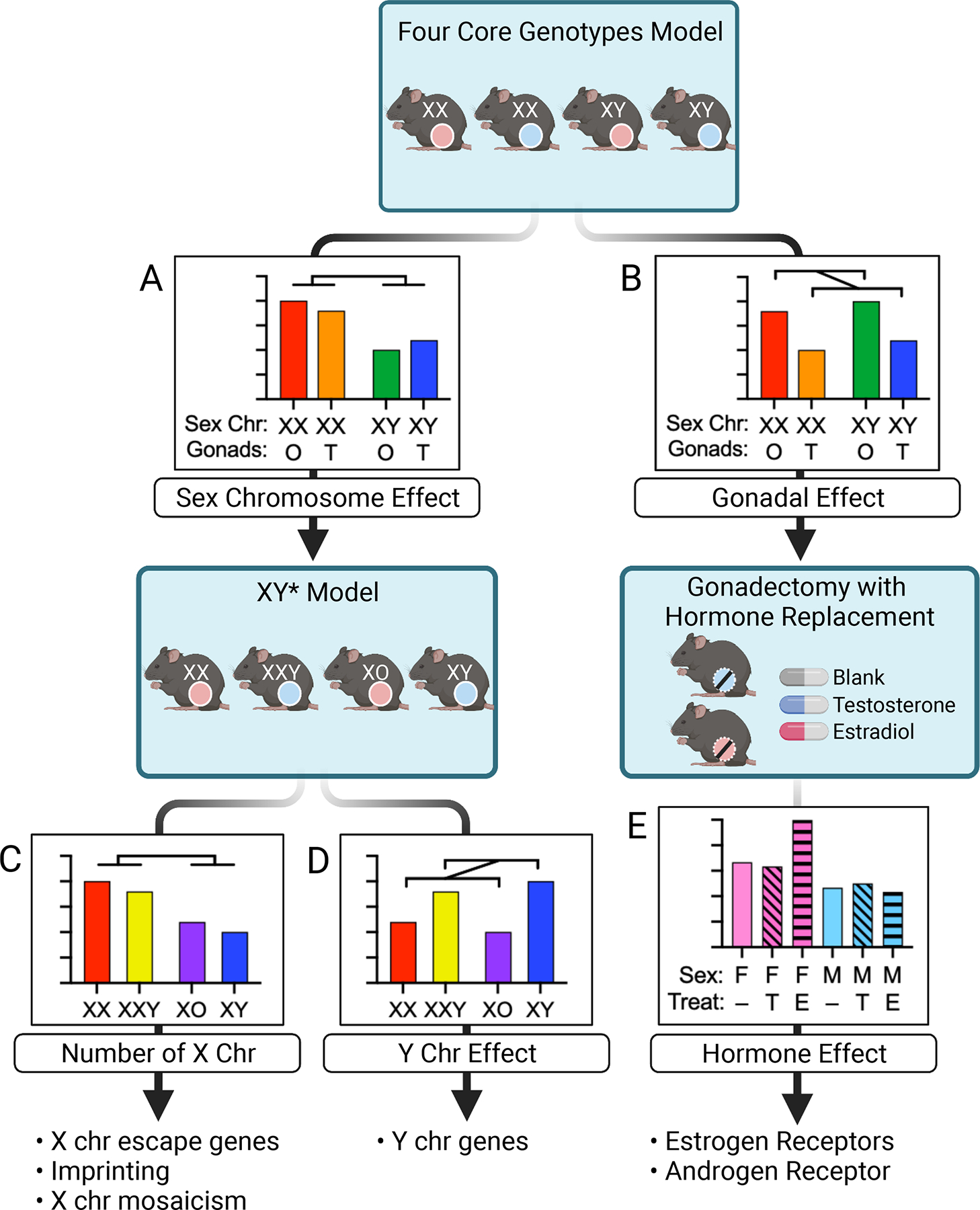
Phenotypic analysis in the Four Core Genotypes model may reveal an effect of sex chromosome complement (XX vs. XY) (A), gonad type (ovaries denoted by pink circles and testes by blue circles) (B), or a combination or interaction between the two (not shown). If sex chromosomes are implicated, subsequent studies in the XY* model differentiates the role of X chromosome number (C) from Y chromosome number (D). Follow-up studies may focus on X or Y chromosome genes. If data from FCG mice indicates a gonadal effect, subsequent gonadectomy and hormone replacement will confirm the gonadal effect and further delineate the role of hormones such as estradiol and testosterone (E). Follow-up studies may assess hormone receptor action.
