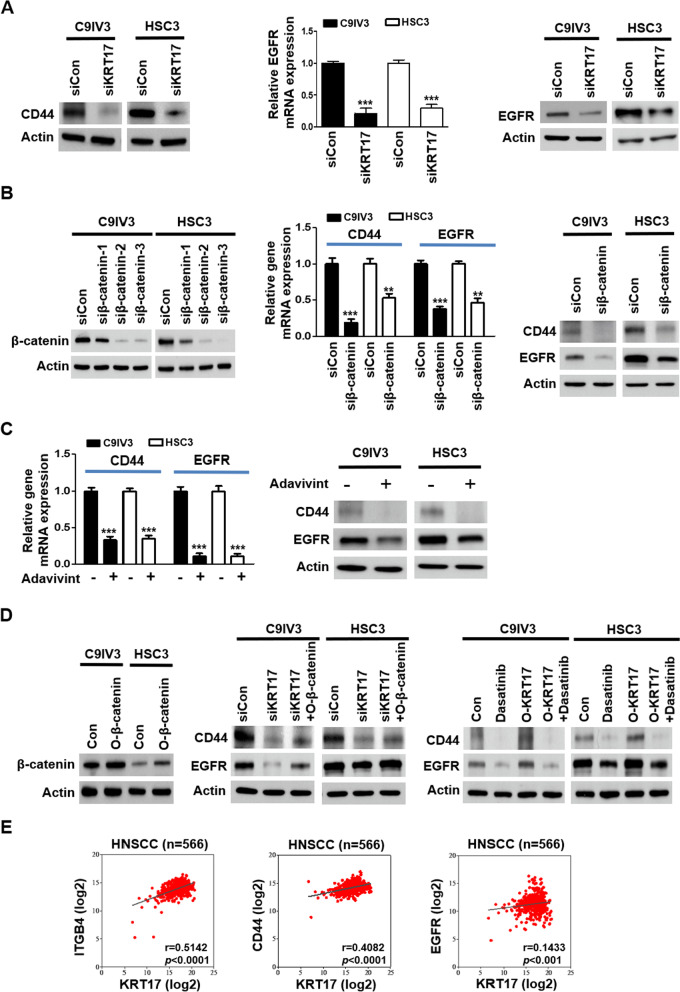
Fig. 4.
KRT17 regulates CD44 and EGFR expression via activations of integrin/Src/β-catenin signaling cascade. A CD44 protein expression in C9IV3 and HSC3 cells transfected with siCon or siKRT17 was determined by western blotting (left panel), and EGFR expression was assessed by qPCR and western blotting (middle and right panels). B Left, Western blotting was used to assess the efficacy of three siRNAs (siβ-catenin-1, -2, -3) designed to specifically silence β-catenin in C9IV3 and HSC3 cells (left panel). Siβ-catenin-2 (siβ-catenin) that caused most effective β-catenin suppression was utilized to examine mRNA and protein expression of CD44 and EGFR in C9IV3 and HSC3 cells (middle and right). C The canonical Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor, adavivint (1 μM), was used to treat C9IV3 and HSC3 cells for 48 h before analyzing expressions of CD44 and EGFR at both mRNA and protein levels. D Expression efficiency of the β-catenin cDNA plasmid (O-β-catenin) was determined at protein level (left panel) prior to combinatorial treatment with either siKRT17 (middle panel) or dasatinib (right panel) for assessing their impacts on CD44 and EGFR expression in C9IV3 and HSC3 cells. Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA or plasmids for 24 h, and then treated with 1 μM dasatinib for 48 h. E Correlation between the gene expression levels of KRT17 and ITGB4, CD44 or EGFR in clinical HNSCC specimens using TCGA database (n = 566)