Figure 2:
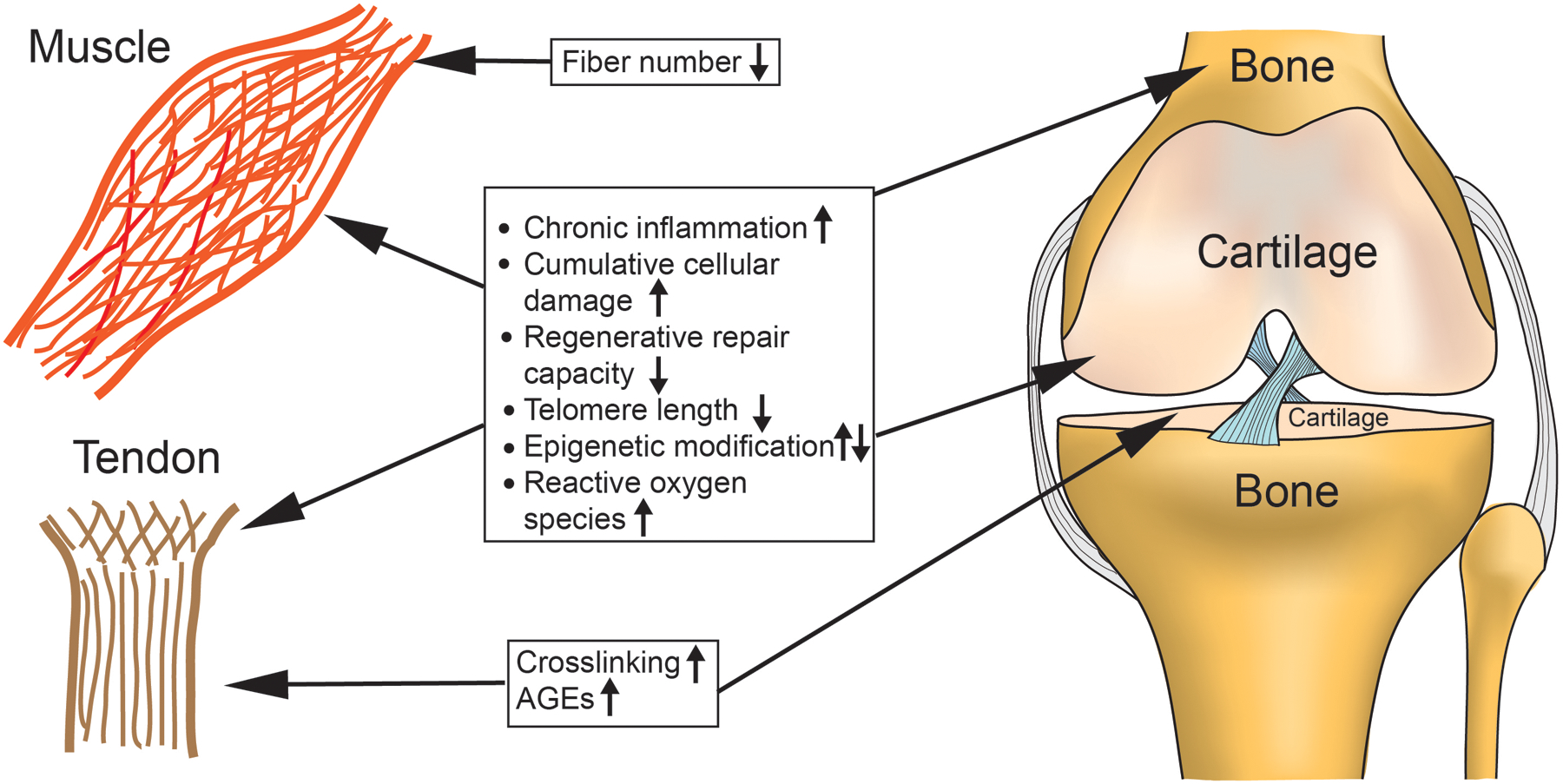
Proposed mechanisms of musculoskeletal aging. Chronic inflammation and catabolic pathway activation, cumulative cellular damage, decreased repair/regeneration, telomere shortening, epigenetic modifications and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) are common pathways amongst many tissues of the musculoskeletal system. Age-associated fiber loss is unique to muscle aging, while crosslinking affects primarily tendons and cartilage.
