Figure 8. Mutation of rhA3C amino acids 44, 45, and 144 to hA3C amino acids enables dimerization.
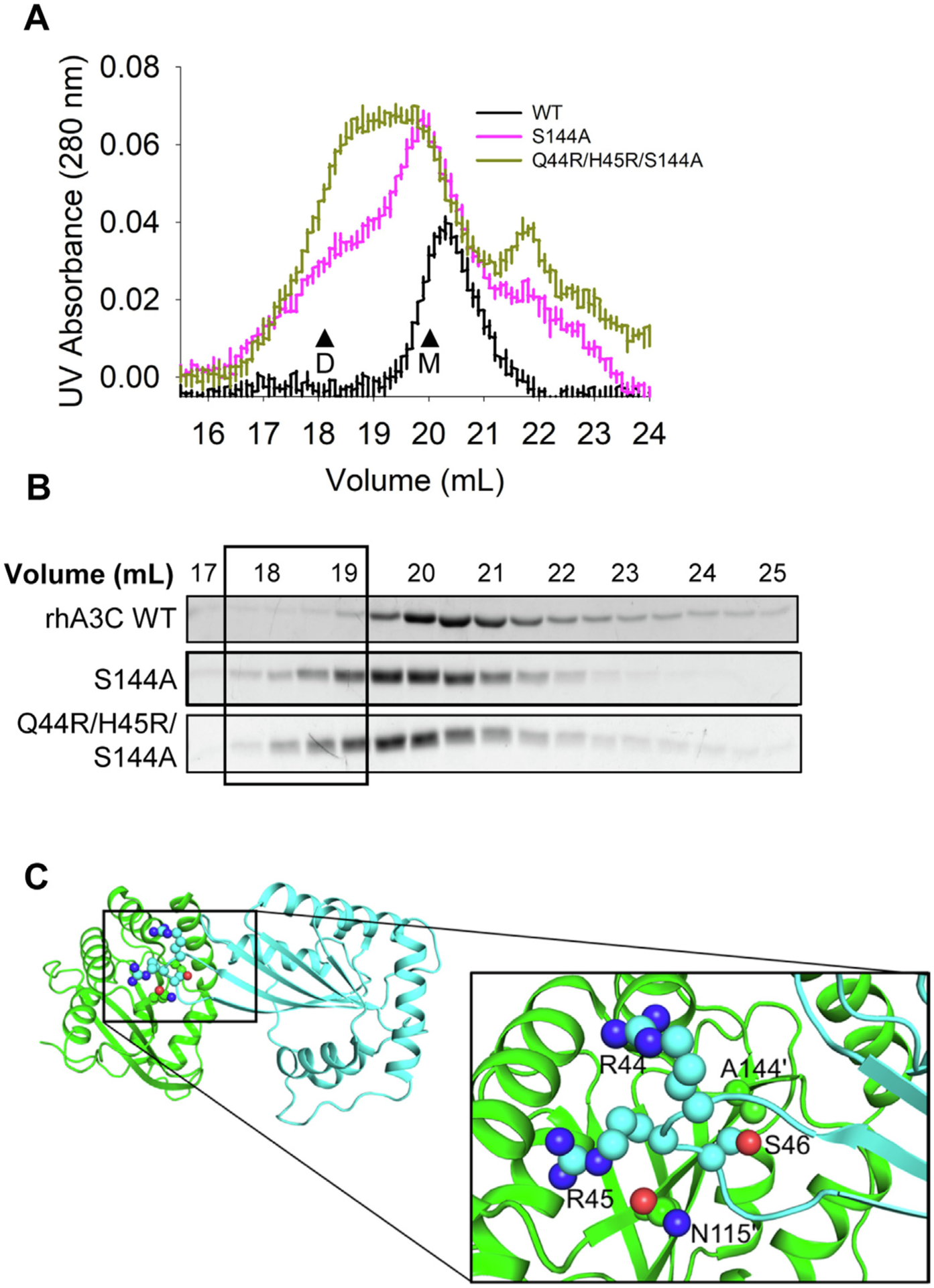
(A) SEC profile for rhA3C WT and rhA3C mutants S144A, and Q44R/H45R/S144A. Elution profiles for rhA3C WT was composed of a monomer peak (M, ~20 ml elution volume). The rhA3C S144A showed a monomer and dimer peak (D, ~19 mL elution volume). Only for the rhA3C Q44R/H45R/S144A there was a more prominent dimer peak. The elution profiles are shown as the UV absorbance during SEC elution. (B) Coomassie stained protein fractions resolved by SDS-PAGE that correspond to the eluted fractions in (A). Box shows where the dimeric fractions eluted. (C) The hA3C 3VOW structure is shown with amino acids important for rhA3C dimerization shown on each monomer. The monomer shown in green has amino acids labeled with a prime symbol to differentiate them from amino acids belonging to the cyan monomer.
