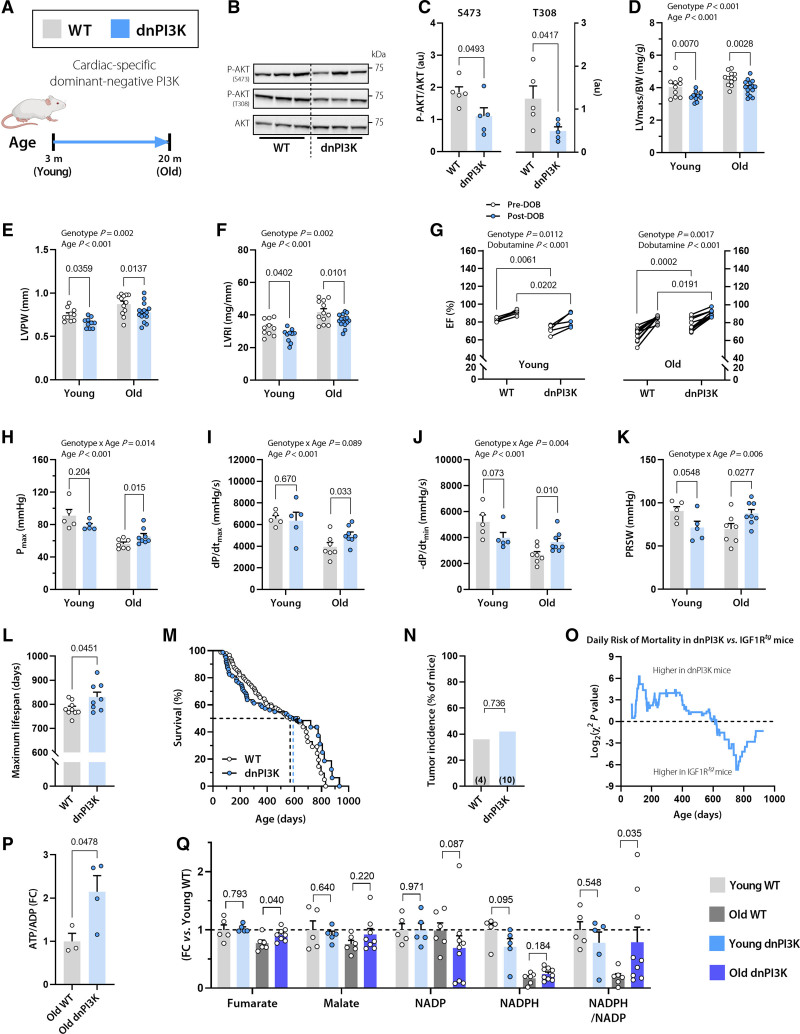
Figure 4.
Reduced cardiomyocyte IGF1R signaling in dnPI3K mice delays cardiac growth, but protects from age-related decline in cardiac function. A, Dominant negative PI3K (dnPI3K) male mice with reduced cardiomyocyte-specific IGF1R signaling and their WT littermates (FVB/N background) were subjected to a comprehensive assessment of cardiac function and structure at the age of 3 months (young) and 20 months (old). B and C, Representative Western blots (B) and quantification of (C) cardiac AKT phosphorylation at Ser473 and Thr308 normalized to total AKT expression in 10-month-old dnPI3K and WT mice (n=5 mice per group). D through F, Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular (LV) mass normalized to body weight (BW; D), LV posterior wall thickness (LVPW; E), and LV remodeling index (LVRI; F) in young and old dnPI3K and WT mice (n=10 young and 12–15 old mice per genotype). G, LV ejection fraction (LVEF) before and after β-adrenergic stimulation by intraperitoneal injection of dobutamine (1.5 mg/kg IP) in young (Left) and old (Right) dnPI3K and WT mice (n=5 young and n=10 old mice per genotype). H through K, Invasive assessment of LV maximum pressure (Pmax; H), maximum rate of pressure rise (dP/dtmax; I), maximum rate of pressure decay (dP/dtmin; J), and preload recruitable stroke work (PRSW; K) in young and old dnPI3K and WT mice (n=5–8 mice per group). L, Maximum lifespan was calculated as the average lifespan of the longest-lived decile in dnPI3K and WT mice (n=8/9 mice per genotype, respectively). M, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis in dnPI3K and WT mice (n=80/90 mice per genotype, respectively). The same WT control group as in Figure 1N was used. Median survival is indicated by the corresponding dashed lines (also see Table S3 for further details). N, Tumor incidence detected by gross necropsy in dnPI3K and WT mice (26/11 mice per genotype, respectively). Number in brackets indicates the number of mice that developed tumors. O, Daily mortality risk in dnPI3K compared with IGF1Rtg mice (n=80/48 mice per genotype, respectively). P, Cardiac abundance of ATP/ADP ratio in 20-month-old dnPI3K and WT mice (n=4–5 mice per genotype). Q, Relative difference in the tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates, fumarate and malate, and the ratio between reduced and oxidized forms of the cofactor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH/NADP) in young (3 months old) and old (20 months old) dnPI3K and WT mice (n=5–9 mice per group). Indicated P values on top of D through K represent factor comparisons by 2-way ANOVA including genotype and age as fixed factors (D–F, H–K) or genotype and dobutamine (G), followed by simple main effects analysis of pairwise comparisons between dnPI3K and their age- or treatment-matched WT controls. Other P values were calculated by the Welch t test or Mann-Whitney test, as appropriate (L, P through Q) or χ2 test (N). Bars and error bars show means and SEM, respectively, with individual data points superimposed. dnPI3K indicates mice harboring an inactivated (dominant negative, dn) p110α isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase; IGF1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IGF1R, IGF1 receptor; IGF1Rtg mice, mice overexpressing human IGF1R specifically in cardiomyocytes; and WT, wild-type.