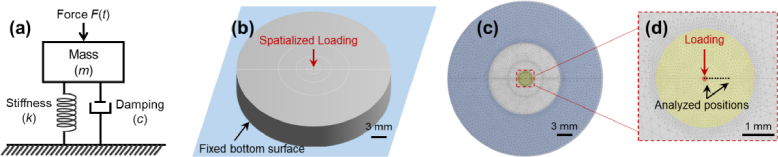
Fig. 4.
Finite element analysis (FEA) model for the phantom. (a) Schematic of a Voigt spring-mass-damper model. F(t) is the force, k is the spring stiffness coefficient, c is the viscous damping coefficient, and m is the mass. (b) Schematic of the phantom geometry and boundary conditions. (c) and (d) show the global view and local view of the FEA model, respectively. The stimulation was applied in the center of the phantom, and the dynamic response was analyzed at seven selected points at the top surface of the phantom at distances of 0–0.5 mm from the center.