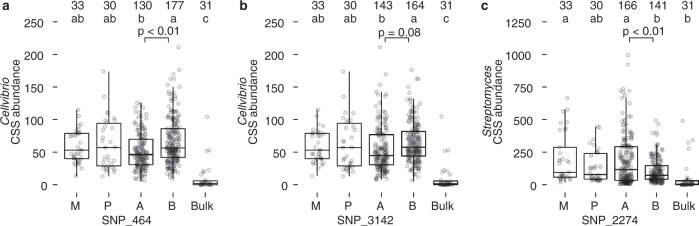
Fig. 5. Validation of Cellvibrio and Streptomyces 16S rRNA QTLs with bulk segregant analysis.
A total of 77 RIL accessions were grown with approximately four biological replicates per accession, as well as 33 modern, 30 wild and 31 bulk samples (see Supplementary Data 13). The number of replicates representing for each treatment is detailed in the top row of each panel. The number of replicates within the RIL population is represented by either an A (modern) or B (wild) allele, which depends on the marker in question. The row below represents the statistical group based on Tukey’s HSD. In addition to the scatter plot, data are presented with boxplots representing the median value, the interquartile range, and whiskers representing the minimal and maximal values excluding points greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range. a The CSS normalized abundances of Cellvibrio 16S rRNA in bulk soil (B), modern (M), wild (W), and RIL accessions at marker position 464 on chromosome 1. At this position, 32 and 45 RIL accessions with modern (A) and wild alleles (B) were used (130 and 177 samples with biological replication respectively). ANOVA showed a statistical difference between genotypes and bulk soil (F(4, 396) = 21.56, p = 4.16 e−16), A post hoc Tukey test supported the conclusion that wild allele at markers 464 associated with increased abundance Cellvibrio (p = 3.913 e−04). b Similarly, for marker 3142 on chromosome 9, there were a total of 35 and 42 RIL accessions with modern (A) and wild alleles (B), (143 and 164 samples with biological replication respectively). ANOVA showed a statistical difference between genotypes and bulk soil (F(4, 396) = 18.43, p = 6.68 e−14), A post hoc Tukey HSD test supported the conclusion that wild allele at markers 464 associated with increased abundance Cellvibrio (p = 0.08). c The normalized CSS abundances of Streptomyces 16S rRNA and sequences in bulk soil (B), modern (M), wild (W), and RIL accessions at marker 2274 on chromosome 6. There was a total of 42 and 35 RIL accessions with modern (A) and wild alleles (B), (166 and 141 samples with biological replication respectively). ANOVA showed a statistical difference between genotypes and bulk soil (F(4, 396) = 8.423, p = 1.57 e−06), A post hoc Tukey HSD test supported the conclusion that wild allele at markers 464 associated with increased abundance Streptomyces (p = 1.152 e−04). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.