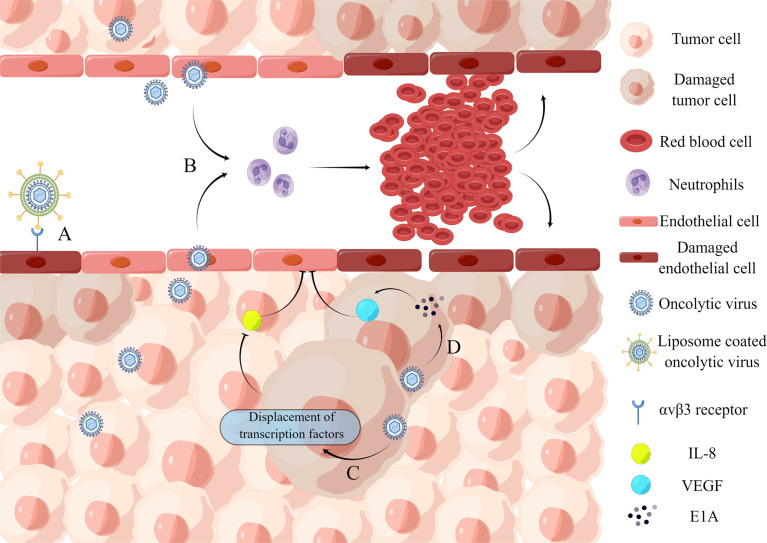
Figure 2.
Inhibition of intra-tumor angiogenesis. (A) Binding of iRGD liposome-encapsulated oncolytic virus to αvβ3 receptor directly induces lysis of HUVECs. (B) Oncolytic virus infection causes the recruitment of a large number of neutrophils and the formation of microthrombosis, resulting in the loss of blood perfusion and the increase of tumor cell apoptosis caused by ischemia. (C) Oncolytic virus dl922-947 treatment reduces IL-8 production in ATC cell lines by displacing the transcription factor NF-κB p65 from the IL8 promoter, thereby inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. (D) Adenovirus can express E1A protein, which can downregulate VEGF by interacting with angiogenic proteins, thereby affecting neointima in the tumor microenvironment and ultimately achieving tumor lysis.