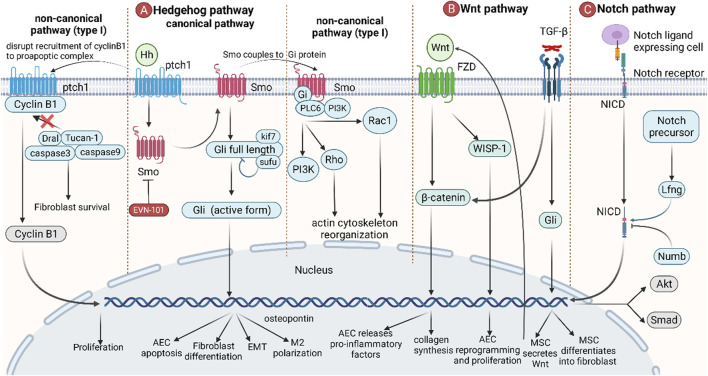
FIGURE 5.
The role of developmental pathways in IPF. (A) Canonical hedgehog pathways start from the binding of Hh to ptch1, and Smo then migrates to the plasma membrane, releasing and activating full-length Gli, which leads to AEC apoptosis, fibroblast differentiation, EMT, and M2 polarization. In non-canonical hedgehog pathways (type I), binding of Hh to ptch1 blocks the recruitment of the pro-apoptotic complex by cyclin B1, resulting in anti-apoptosis and promotion of cell proliferation. In non-canonical hedgehog pathways (type II), Smo is coupled to Gi protein, activating downstream PI3K, Rho, and Rac1, resulting in an increase in intracellular calcium concentration and a rearrangement of the cytoskeleton. (B) Wnt promotes the accumulation of β-catenin by binding to FZD, thereby stimulating AECs to release proinflammatory factors and promote collagen synthesis in fibroblasts. Wnt also directly induces AEC reprogramming and proliferation via WISP-1. TGF-β can induce MSCs to secrete Wnt and promote MSC differentiation. (C) The Notch ligand binds to the Notch receptor, causing the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) of the Notch receptor to break and enter the nucleus, leading to gene transcription. Lfng positively regulates this process, while Numb negatively regulates this process. Wnt is also involved in the regulation of Akt and Smad pathways.