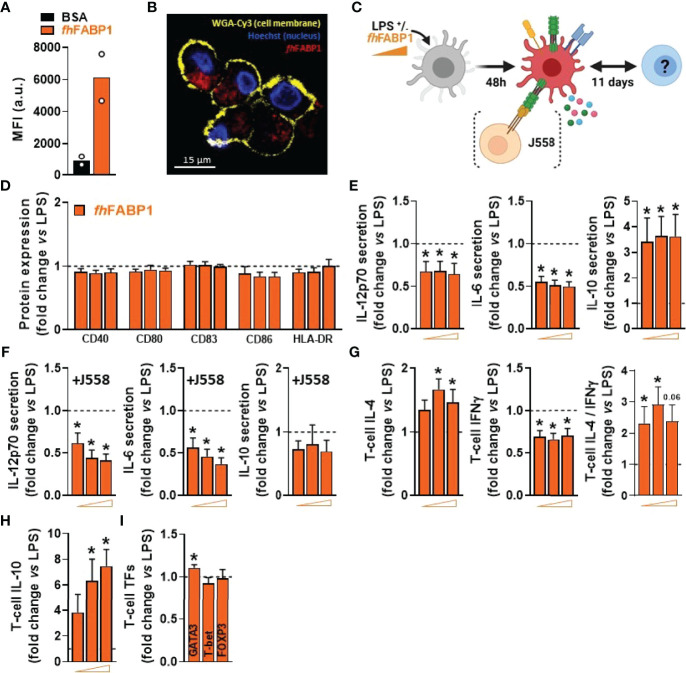
Figure 3.
Fasciola hepatica FABP1 reduces the inflammatory phenotype of LPS-stimulated dendritic cells and increases both Th2-on-Th1 ratio and IL-10-producing T cells. The binding of PF-647-labeled BSA-control (black bar) or recombinant fhFABP1 (orange bars) to monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs) was assessed after 2 hours by flow cytometry (A) The subcellular localization of PF-647-labeled recombinant fhFABP1 (depicted in red) in moDCs was determined after 4 hours by confocal microscopy and shown as 2D images of Z-planes with nuclear (Hoechst, depicted in blue) and membrane (WGA-Cy3, depicted in yellow) staining (B) One representative experiment is shown from 3 independent experiments Human moDCs were treated for 48 h with increasing concentration of fhFABP1 (10, 25, 50 µg/ml) in presence of LPS (100 ng/ml) and either co-cultured with CD40-L-expressing cell line J558 for 24 hours or co-cultured with naïve CD4+ T cells for 11 days (C) The cell-surface expression of co-stimulatory molecules (D) and cytokines secretion by moDCs with (E) or without co-culture with J558 (F) were determined by flow cytometry and ELISA, respectively Conditioned moDCs were characterized for their capacity to prime CD4+ T cell responses, as described in Figure 1 (G). One representative experiment is shown for the Zebra plot In addition, primed CD4+ T cells were restimulated with α-CD3 and α-CD28 to measure IL-10 production after 24 hours (H) and analysed for GATA3, T-bet, and FOXP3 transcription factor expression by flow cytometry (I). All data are expressed relative to the DCs stimulated with LPS alone (dash line) as mean ± SEM * P ≤ 005 vs LPS alone (n=3-7 independent experiments).