Figure 5.
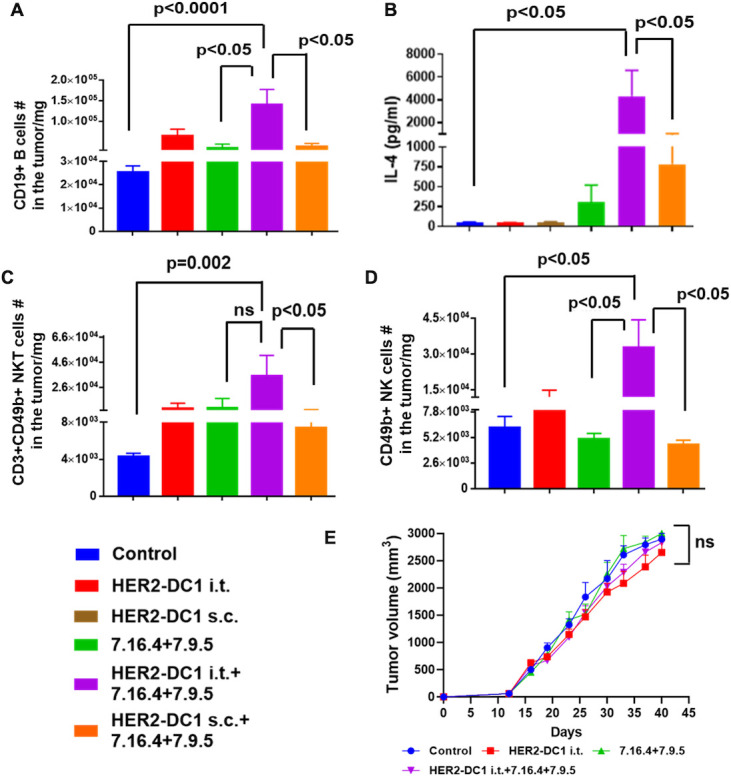
HER2-DC1 i.t. in combination with anti-HER2 antibodies treatment induces B, NKT and NK cells tumor infiltration and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. (A) Tumors from the experimental mice were collected on day 60 after completion of treatments, single cell suspensions were stained for CD19+ B cells as described in the methods and analyzed using flow cytometry. (B) Serum level of IL-4 in the experiment groups was analyzed by Th cytokine flow cytometry array. (C) Level of tumor infiltrating CD3+CD49 b (DX-5)+double positive NKT cells. (D) Tumor infiltrating level of CD49b (DX-5)+NK cells. Results were shown as mean±SEM of at least three independent experiments. (E) FcγR KO mice were injected with 3×104 TUBO cells orthotopically into the MFP. After tumor establishment, mice were treated with HER2-DC1 i.t. alone or anti-HER2 antibodies (7.16.4 and 7.9.5) alone or combination of both as described in methods. Tumor growth was monitored two times a week (n=8). Mean±SEM. HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HER2-DC1, HER2 peptide-pulsed type 1 polarized dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; i.t., intratumoral; MFP, mammary fat pad; NK, natural killer; ns, not significant; s.c., subcutaneous; NKT, natural killer T cells.
