Figure 3. Deletion of GSNOR impairs the repopulating ability of HSCs.
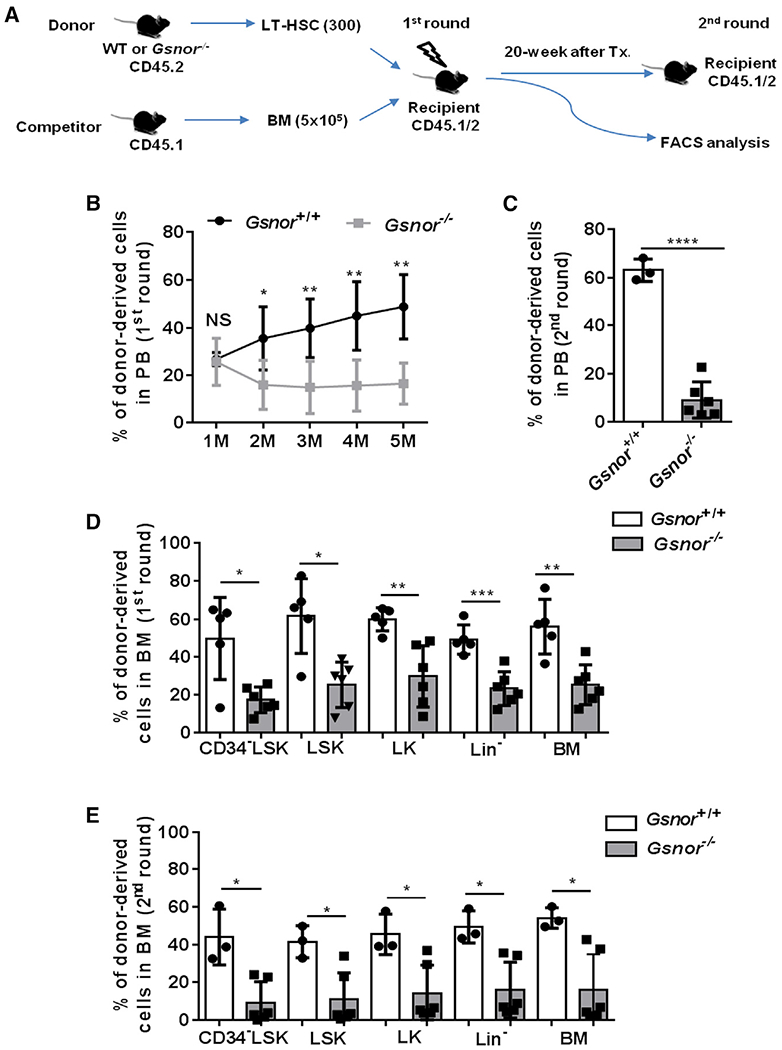
(A) Schematic diagram showing the serial competitive transplantation assay. In brief, 300 LT-HSCs from Gsnor+/+ mice or Gsnor−/− mice (2 to 3 months old; CD45.2) were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients (CD45.1/2) along with 5 × 105 competitor BM cells (CD45.1). 5 months post-transplantation, 1 × 106 BM cells from the primary recipients were transplanted into the second round of recipient mice.
(B and C) The chimerism of donor-derived cells in PB was examined at the indicated time points after the first and second round of transplantation (n = 3–6 recipients per group).
(D) The chimerisms of donor-derived cells in the indicated populations were analyzed at 5 months after the primary transplantation (n = 5–6 per group).
(E) The chimerisms of donor-derived cells in the indicated populations were analyzed at 8 months after the 2nd transplantation (n = 3–6 per group).
(B–E) Data were tested for normal distribution via Shapiro-Wilk normality test. Statistical significance of the two groups of normally distributed data was assessed by Student’s t test with Welch’s correction (C and D). Logit transformation was performed with the non-normally distributed data, and the Shapiro-Wilk normality test was used for testing the normal distribution. Student’s t test with Welch’s correction was used to compare the statistical significance of the logit-transformed normally distributed data (B). Statistical significance of the non-normally distributed data was assessed by Wilcoxon/Mann-Whitney test (E). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; NS, not significant.
