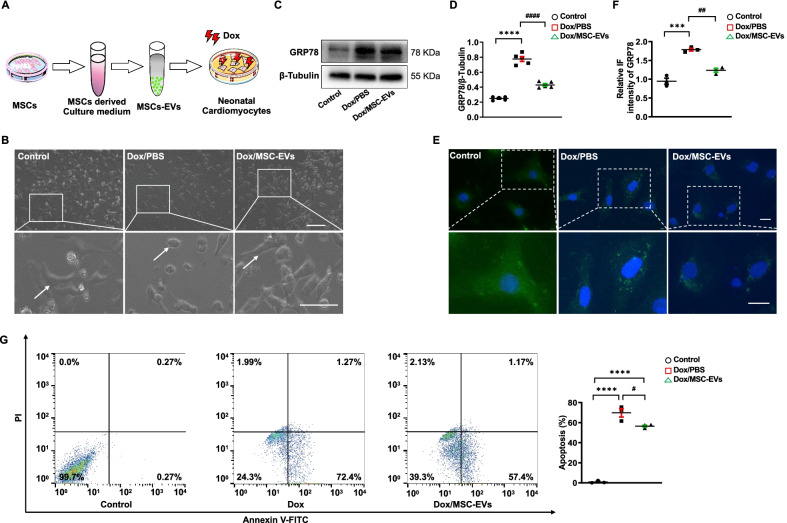
Fig. 3.
MSC-derived extracellular vesicles decline ER stress-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. A. Experimental scheme of the design of the in vitro study. Extracellular vesicles derived from MSCs (MSC-EVs, 200 μmol/L), Dox (8 μmol/L). B. Representative bright-field images of cardiomyocytes exposed to PBS (control), Dox/PBS, or Dox/MSC-EVs. Injured cardiomyocytes were identified by bright arrows. Scale bar, 100 μm. C and D. Western Blotting and quantified GRP78 expression in cardiomyocytes exposed to PBS (Control), Dox/PBS, or Dox/MSC-EVs (n = 5). ****P < 0.0001 vs Control, ####P < 0.0001 vs Dox/PBS. E. Representative immunofluorescence images of antibody to GRP78 (green) binding to cardiomyocytes exposed to PBS (Control), Dox/PBS, or Dox/MSC-EVs. Scale bar, 25 μm. F. Statistics of the fluorescence intensity of GRP78 in each group (n = 3). ***P < 0.001 vs Control, ##P < 0.01 vs Dox/PBS. G. Representative Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and quantitative apoptotic proportion of cardiomyocytes exposed to PBS (control), Dox/PBS, or Dox/MSC-EVs (n = 3). ****P < 0.0001 vs Control, #P < 0.05 vs Dox/PBS. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, unless specifically indicated