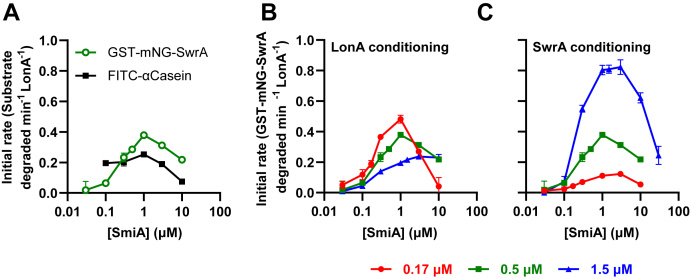
Figure 4.
SmiA stimulates SwrA proteolysis but becomes generally inhibitory at high concentration.A, the rate of 0.5 μM GST-mNG-SwrA (green) and 0.25 μM FITC-α-casein (black) proteolysis as a function of SmiA concentration in the presence of 0.5 μM LonA hexamers. B, the rate of 0.5 μM GST-mNG-SwrA degradation as a function of SmiA concentration in the presence of 0.17 μM (red), 0.5 μM (green), and 1.5 μM (blue) LonA hexamers. C, the rate of 0.17 μM (red), 0.5 μM (green), and 1.5 μM (blue) of GST-mNG-SwrA degradation as a function of SmiA concentration in the presence 0.5 μM LonA hexamers. Relative fluorescence was converted to molecules of fluorescent substrate using a standard curve (Fig. S1), and initial velocity was derived from the maximum slope of each degradation curve. Each data point represents the average rate of in vitro turnover assays performed in triplicate, and error bars represent SD. GST, glutathione-S-transferase.