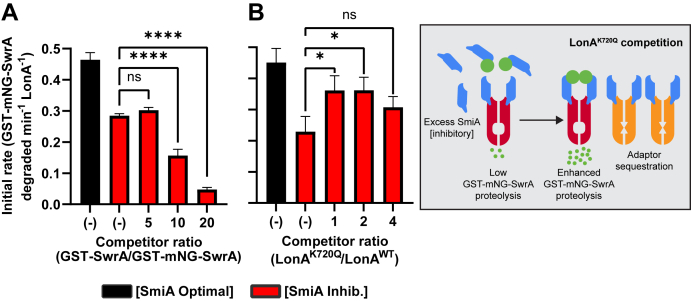
Figure 5.
GST-mNeonGreen SwrA proteolysis can be competitively inhibited either by the addition of unlabeled substrate or an active-site mutant of LonA.A, rate of 0.5 μM GST-mNG-SwrA proteolysis in the presence 0.5 μM SmiA and 0.5 μM LonA and competitor GST-SwrA expressed as a concentration ratio relative to the fluorescent substrate. B, left, rate of 0.5 μM GST-mNG-SwrA proteolysis in the presence of 0.5 μM SmiA and 0.5 μM LonA plus competitor LonAK720Q-His levels expressed as a ratio relative to functional enzyme. B, right, excess SmiA (blue) inhibits LonA (red) degradation of GST-mNG-SwrA (green). Addition of inactive LonAK720Q (orange) sequesters excess SmiA and restores GST-mNG-SwrA proteolysis. Each data point represents the average rate of in vitro turnover assays performed in triplicate, and error bars represent the SD. Statistical analysis: ∗ indicates a difference significance of p = 0.0014, ∗∗∗∗ indicates a difference significance of p < 0.0001; ns indicates that the difference is not significant. GST, glutathione-S-transferase.