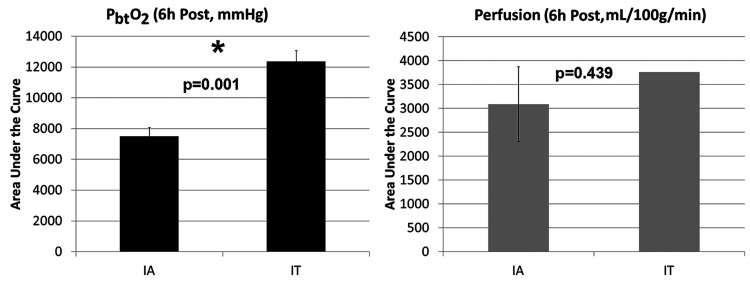
FIG. 2.
Improvement of brain oxygenation and blood flow after administration of intrathecal nicardipine as compared with intraarterial procedures. We performed an AUC analysis to quantitatively compare the effect of intrathecal nicardipine with intraarterial procedures on focal cerebral oxygenation and blood flow as measured with Licox and Hemedex probes, respectively. For this analysis, oxygenation and blood flow values were compared for the 6 hours after the respective interventions. A 2-sample t-test was used to compare PbtO2 values, but because perfusion monitoring was performed only after a single administration of intrathecal nicardipine, the AUC values subsequent to the intraarterial procedures were compared with the single AUC value obtained after the intrathecal nicardipine administration. For this analysis, the five intraarterial procedures performed before the initiation of intrathecal nicardipine were compared with values subsequent to the five intrathecal administrations. Both brain oxygenation and blood flow were greater after intrathecal nicardipine administration than after intraarterial procedures; this difference was significant for PbtO2 values (*p = 0.001).