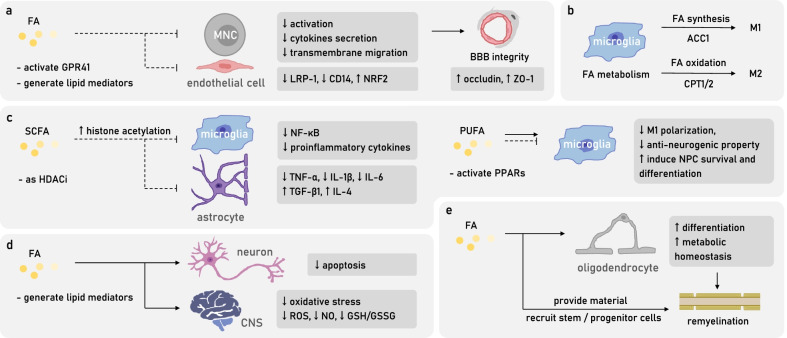
Fig. 3.
FAs with multifaceted roles in MS CNS pathogenesis. a FAs, by inhibiting the inflammation-induced MNCs activation and migration, as well as by alleviating oxidative stress of endothelial cells, help to preserve BBB integrity during the pathogenic state. b FA metabolism modulates the polarization of microglia, which are critical contributors of MS late-stage CNS lesions. c FAs regulate CNS resident glia by introducing them to an anti-inflammatory and pro-neurogenic state. d FAs reduce neuron apoptosis and CNS oxidative stress. e FAs promote remyelination by providing raw materials, recruiting stem cells and progenitor cells, and by favoring oligodendrocytes differentiation and metabolic homeostasis. BBB blood–brain barrier, CNS central nervous system, MNC mononuclear cell