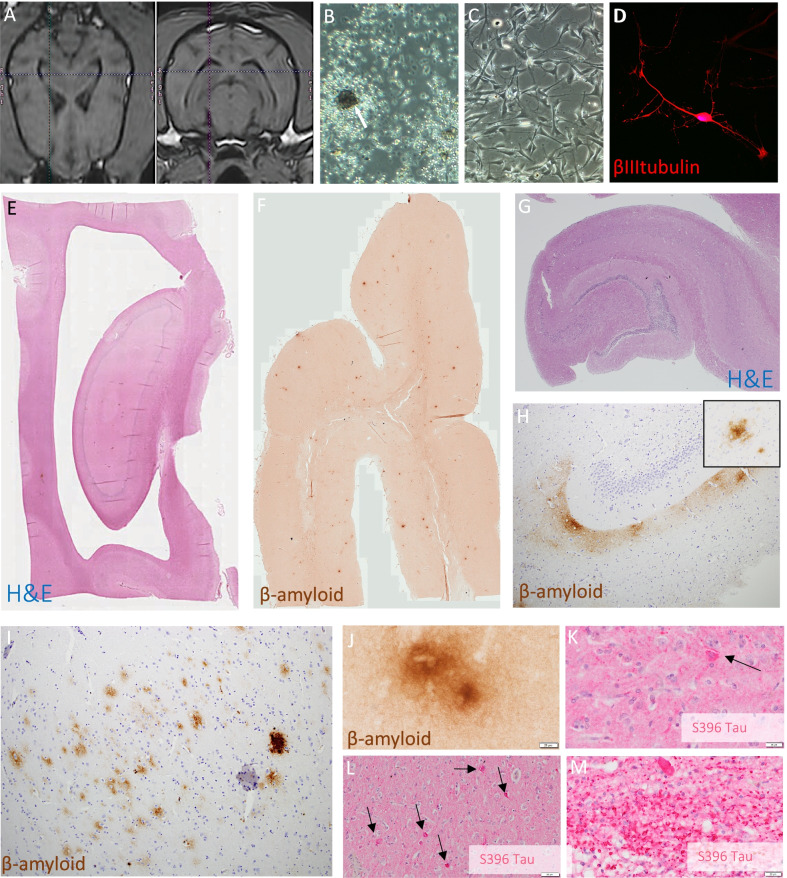
Fig. 2.
Patient-specific SKN cell therapy is safe over long term and does not impact AD pathology. A Orthogonal MRI slices show targeting of SKN microinjection in canine dorsal hippocampus (Timmy; see Additional file 1: Materials for panel with targeting for all canine patients). B Characteristic cell morphology of SKNs at neurosphere suspension phase (arrow identifies a neurosphere from Grover cell line), and C adherent expansion phase at which point cells are harvested and engrafted (Timmy cell line). D SKN cell following 21 days in vitro neuronal differentiation in Leo cell line showing typical neuronal morphology and marker expression (βIII tubulin; see Additional file 1: Fig. S14 for neurofilament). E H&E image low magnification of hippocampus shows normal cytoarchitecture in Grover at post mortem (4-months follow up). F β-amyloid Alzheimer disease plaque pathology in Grover frontal lobe low magnification. G Normal hippocampal H&E cell histology in Timmy (20-months follow-up). H) β-amyloid pathology in Timmy hippocampus, with insert showing high magnification of a diffuse plaque, and in I) occipital cortex, a combination of diffuse and dense core plaques. J High magnification of β-amyloid diffuse plaque in Grover hippocampus (CA3). K) S396-hyperphosphorylated tau positive inclusions in Grover anterior cingulate and L frontal cortex. M S396-tau positive tauopathy in Grover thalamic white matter bundles cut in cross-section. Grover had the highest tauopathy burden of any dog in our Canine Brain Bank and fastest rate of clinical decline prior to treatment (see Additional file 1: Materials).