Fig. 1.
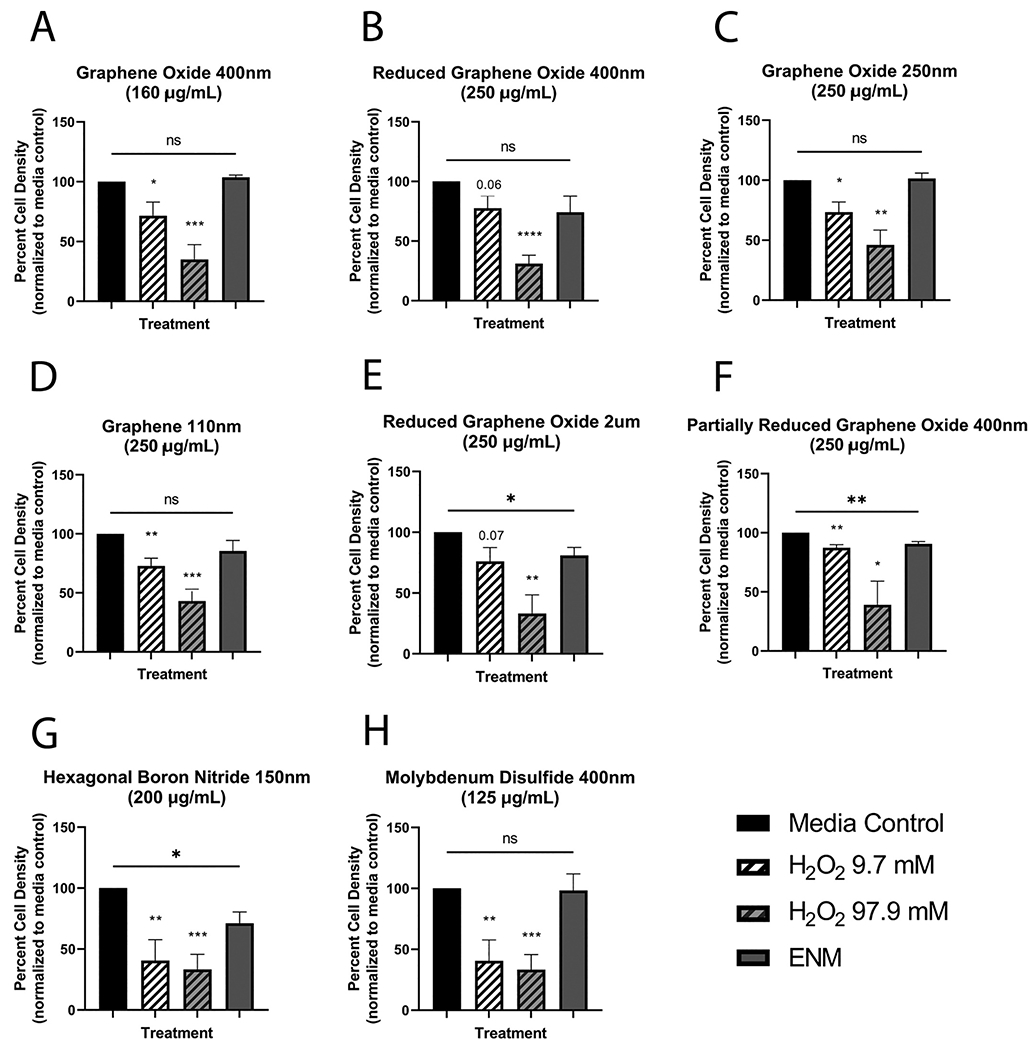
Cytotoxicity of eight 2D engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) in primary mouse tracheal epithelial cell culture as percent cell density. Nanomaterials tested included graphene oxide of two sizes (A & C), reduced graphene oxide of two sizes (B & E), graphene (D), partially reduced graphene oxide (F), hexagonal boron nitride (G), and molybdenum disulfide (H). All density values were normalized to the media control of the respective plate. Cytotoxicity was induced in three ENMs: reduced graphene oxide 2 um (250 μg/mL), partially reduced graphene oxide 400 um (250 μg/mL), and hexagonal boron nitride (200 μg/mL). Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was used as a positive control for cytotoxicity. An unpaired student’s t-test was performed to compare each treated group to the media control group: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. N = 3 (F), N = 4 (C, E), or N = 5 (A, B, D, G, H) for all treatment groups.
