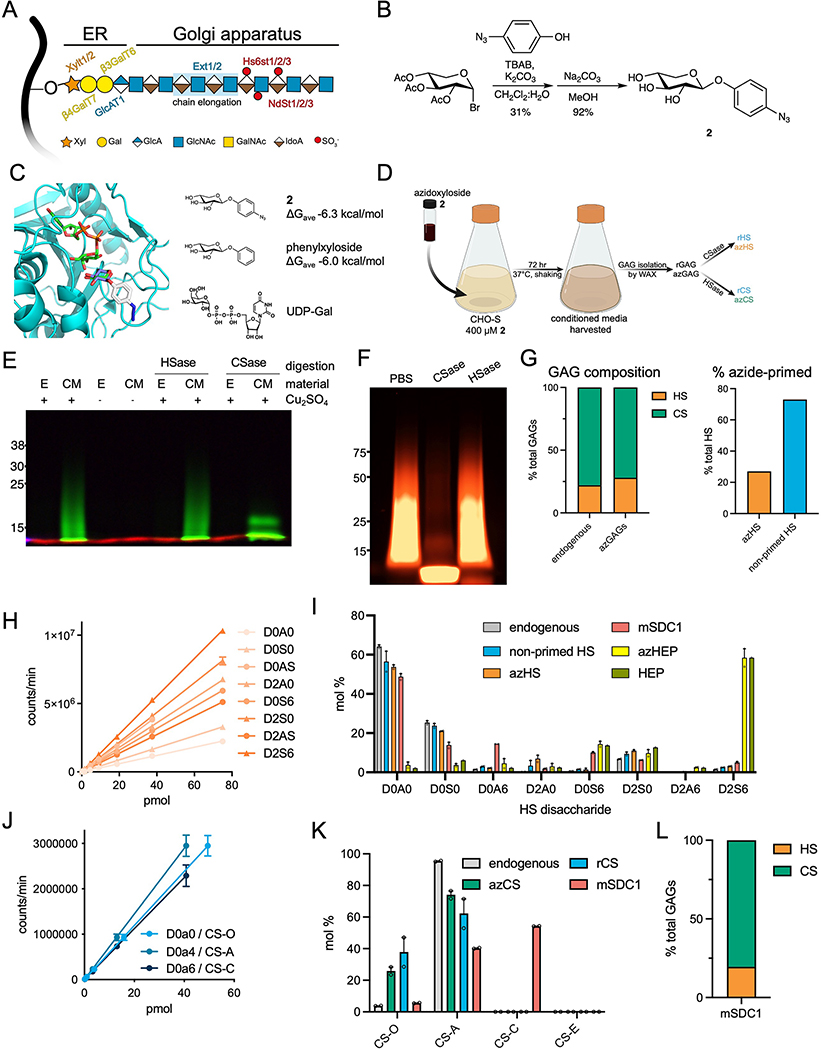
Extended Data Fig. 2.
Characterization of recombinant and azido-GAG (A) Graphical representation of heparan sulfate (HS) glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus. The common HS and CS tetrasaccharide linker (Xyl-Gal-Gal-GlcA) is synthesized in the ER before being elongated by Ext1/2 enzyme complexes to create the HS repeating disaccharide motif. (B) Synthetic strategy to produce azidoxyloside 2. (C) Xyloside 2 was docked (AutoDock Vina) into the active site of β4GalT7 in complex with the UDP-Gal donor (teal, PDB ID 4M4K). Top poses for the docked compounds showed positioning of the xyloside C4 oxygen within 3–4 Å of the C1 atom on the galactose ring of UDP-galactose. The binding affinity of the five lowest energy poses for each simulation was averaged. Comparison of the average binding energies showed the addition of azido group into the aromatic ring component did not exact a substantial binding penalty. (D) Suspension CHO (CHO-S) cells are incubated with 2 (400 μM; 72 hr) and conditioned media is harvested for isolation of soluble recombinant, azido-GAGs (azGAGs). (E) SDS-PAGE analysis using AF546-appended rGAGs confirms that azide-primed GAGs are present mostly in the conditioned medium (CM) compared to cell extracts (E). Selective degradation of rGAGs by chondroitinase (Csase) results in a collapsed signal, indicative of our CM consisting primarily of CS. Representative of two biological replicates, molecular weight ladder in kDa. (F) azGAGs were analyzed by SDS-PAGE after copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) with AF546 fluorophore and digestion with chondroitinase (CSase) or heparinase (HSase). The presence of a collapsed lower molecular-weight band upon CSase digestion suggests large amounts of primed CS. Representative of two biological replicates, molecular weight ladder in kDa. (G) Through dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO) bead capture and subsequent disaccharide analysis, the proportion of azide-functionalized HS (orange) and CS (green) in the rGAG mixture can be quantified, with 27% being azido-HS (azHS), which mimics endogenous GAG ratios. (H) Standard curve of HS disaccharides. (I) Disaccharide analysis of endogenous HS (grey) from untreated cells, soluble non-primed HS (blue), azHS (orange) show similar sulfation profiles. Similarly, functionalization of free heparin (HEP, green) to azido-primed heparin (azHEP, yellow) did not affect sulfation. As expected, heparin is substantially more sulfated than HS. HS chains for mSDC1 (pink) were also analyzed. (J) Standard curve of CS disaccharides. (K) Disaccharide analysis of CS from endogenous (grey), azCS (green), rCS (blue) and mSDC1 (pink). (L) Proportion of CS and HS GAGs isolated from commercial, mammalian expressed mSDC1, calculated by disaccharide analysis. Analyses and graphs generated with GraphPad Prism 9. Bar graphs represent means and error bars represent SEM representative from two technical replicates.