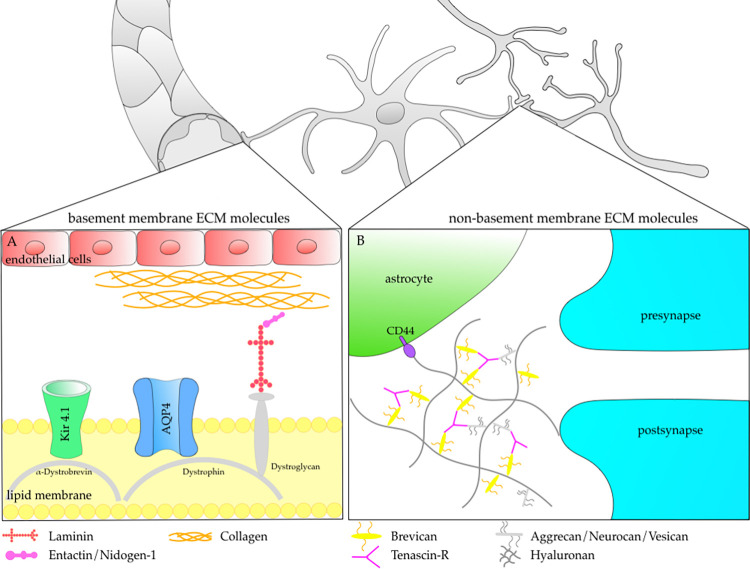
Fig 1. Localization and function of basement membrane and non-basement membrane extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules.
Detailed view (A) shows basement membrane ECM molecules like laminin, entactin/nidogen-1 and collagen. Laminin interacts within the dystroglycan-dystrophin-dystrobrevin complex to ensure anchoring and stabilization of the aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channel as well as the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir 4.1 in the perivascular basal lamina [32, 33]. Detailed view (B) illustrates the participation of non-basement membrane ECM molecules like brevican and tenascin-R in the tripartite synapse. The tripartite synapse consists of a presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane as well as a closely apposed astrocyte process [44]. By connection to further ECM components (hyaluronan, aggrecan, neurocan, vesican) tenascin-R and brevican form perineuronal nets (PNN). Anchored via the cell-surface glycoprotein CD44, PNNs are presumed to play a role in synapse stability and plasticity [44].