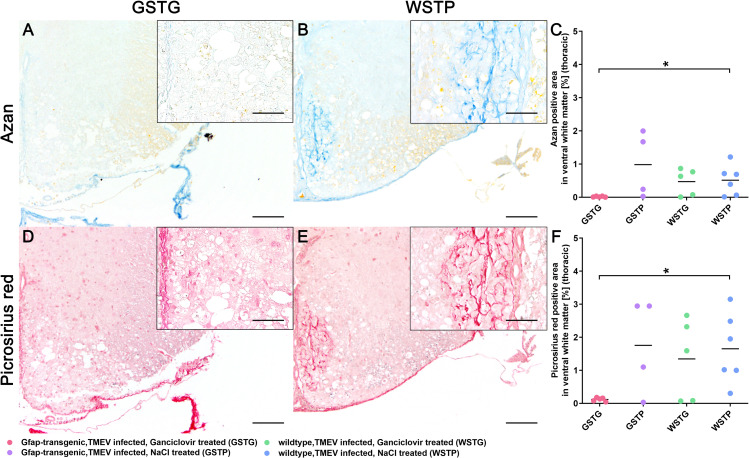
Fig 3. Impact of astrocyte depletion upon the deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM).
Quantification of ECM components in the thoracic spinal cord white matter was performed using azan (A-C) and picrosirius red (D-F) staining. Accumulation of ECM components was detected intralesionally within the ventral part of the thoracic spinal cord white matter. At 77 dpi TMEV infected, ganciclovir treated, GFAP-transgenic mice (GSTG) mice (A, D) showed a significantly reduced azan and picrosirius red positive area, respectively, compared to TMEV infected, natrium chloride (NaCl) treated wildtype (WSTP) animals (B, C, E, F). Inserts visualize in more detail the intralesional accumulation of azan (B) and picrosirius red (E) labeled ECM molecules in WSTP animals compared to astrocyte depleted mice (A, D). For each antibody, one cross section of the thoracic spinal cord was evaluated per animal. Data are shown as scatter dot plots. The horizontal bar indicates the mean. Significant differences between GSTG and the control groups obtained by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Mann–Whitney U post hoc tests are indicated by *, p ≤ 0.05. Bars represent 100 μm in overviews and 50 μm in the inserts.