Figure 3.
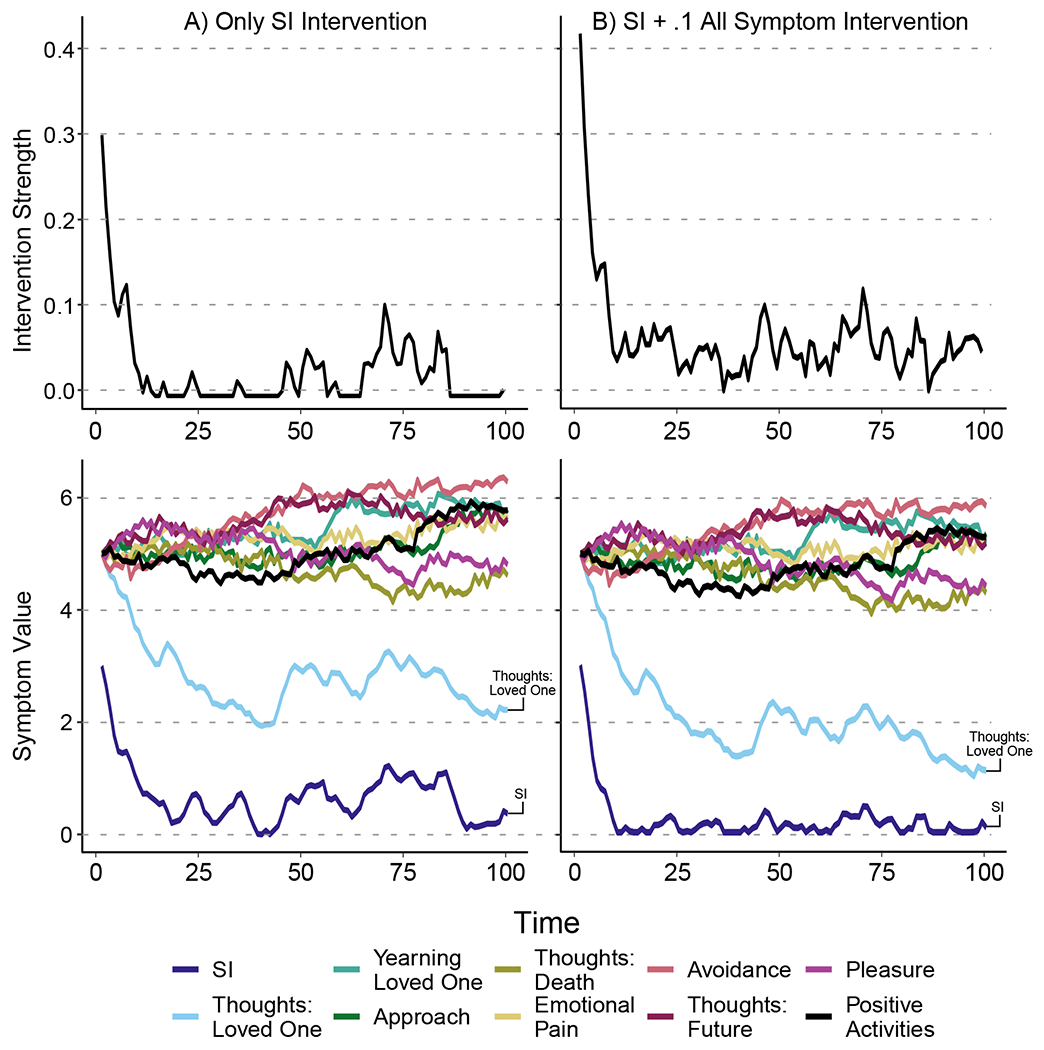
Intervention strength and symptom values when (A) intervening on only suicidal ideation with strength of 1 and (B), when intervening on suicidal ideation with a strength of 1, and all other symptoms with a strength of .1. Note that the same sequence of random disturbances were applied to each simulation. Results show that the broader intervention in Panel B leads to more reduction in suicidal ideation and thoughts: loved ones than the single target intervention in Panel A. Additionally, the broad nature of the intervention in Panel B only reduced the spread of symptoms other than suicidal ideation and thoughts: loved ones slightly more than the single target intervention in Panel A.
