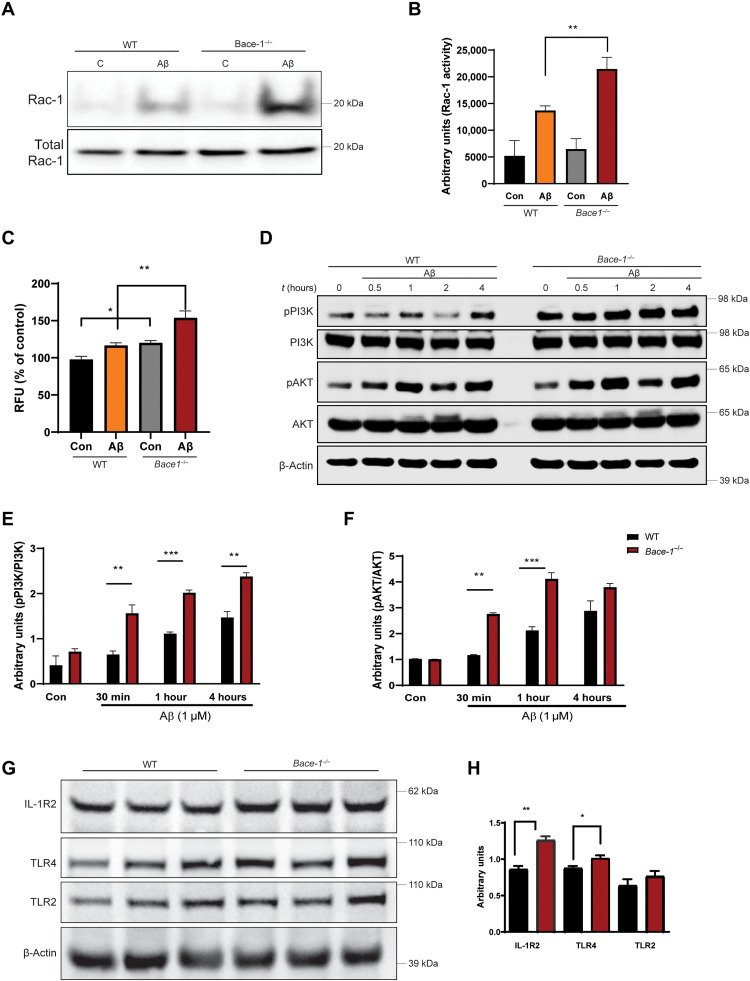
Fig. 7. BACE-1 signaling regulates Aβ uptake by modulating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway.
(A and B) WT and Bace-1–null BMDM were treated with Aβ for 30 min, and Rac-1 activity was determined using the PBD pulldown assay, followed by immunoblotting with an anti–Rac-1 antibody. The bar graph in (B) shows elevation of Rac-1 activity in Bace-1–null BMDM (N = 3, **P < 0.01, Student’s t test). (C) Elevated ROS levels in WT and Bace-1–null BMDM measured spectrophotometrically by changes in DCFDA fluorescence 30 min after Aβ treatment. (D to F) Immunoblot panel and quantification for phosphorylated PI3K (pPI3K) and pAKT, as performed on lysates from WT and Bace-1–null BMDM treated with Aβ (1 μM) for the indicated time points. There was significant up-regulation of pPI3K and pAKT as early as 30 min after Aβ treatment (N = 3, **P < 0.01, Student’s t test). (G and H) Levels of full-length IL-1R2 and TLR4 in the cortex of Bace-1–null brains were elevated, but TLR2 levels were slightly increased (N = 3 independent experiments, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05, Student’s t test), likely related to abolished cleavage of these proteins by BACE-1.