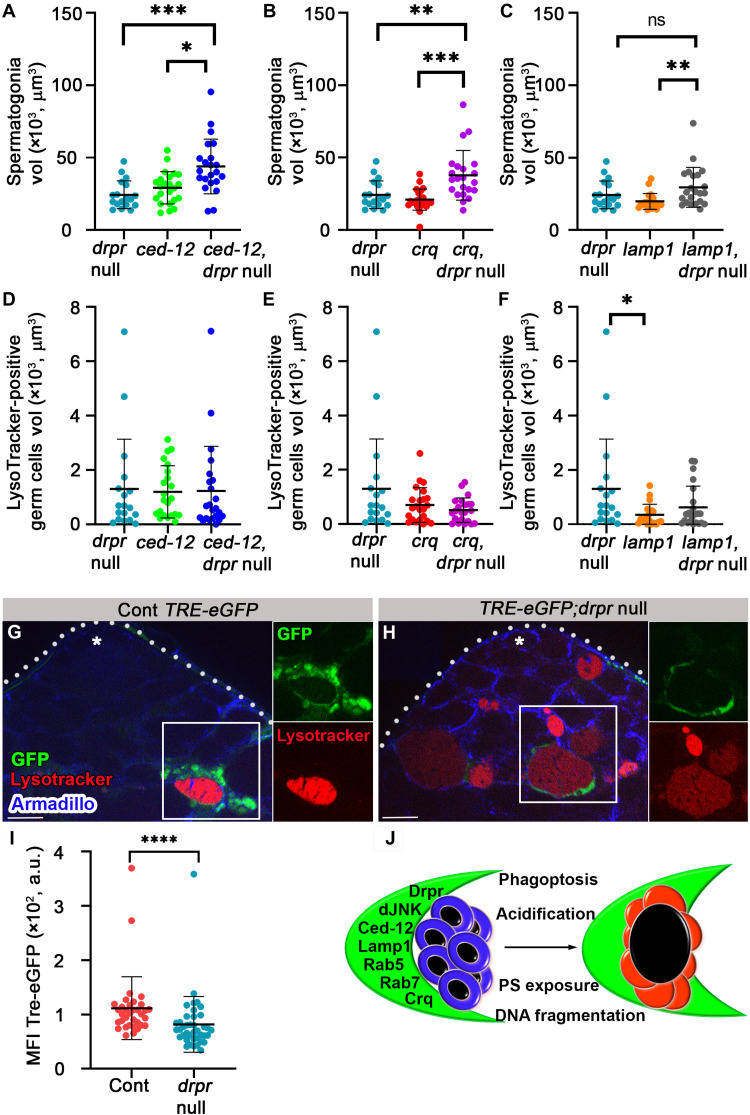
Fig. 9. drpr acts in parallel with ced12 and crq and upstream of lamp1 and dJNK in cyst cells during phagoptosis.
(A to F) Quantification of the volume of live spermatogonia cells (A to C) and LysoTracker-positive germ cells (D to F) as measured with Imaris in testes from drpr null (c587Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/CyO;drpr null, n = 18), ced-12 RNAi (c587-Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/UAS-ced-12 RNAi; drpr null/TM2, n = 23), ced-12 RNAi and drpr-null double mutants (c587-Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/UAS-ced-12 RNAi; drpr null, n = 22), crq RNAi (c587-Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/UAS-crq RNAi; drpr null/TM2, n = 23), crq RNAi and drpr-null double mutants (c587-Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/UAS-crq RNAi; drpr null, n = 22), lamp1 RNAi (c587-Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/UAS-lamp1 RNAi; drpr null/TM2, n = 21), and lamp1 RNAi and drpr-null double mutants (c587-Gal4;UAS-cytGFP/UAS-lamp1 RNAi; drpr null, n = 22). Note that drpr acts in parallel with ced-12 and crq in engulfment and upstream of lamp1. Statistical significance was determined by a Kruskal-Wallis test; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001. (G and H) Expression of TRE-eGFP reporter in wild-type (G) and drpr-null testes (H) labeled with LysoTracker (red) and immunostained for Armadillo (blue, cyst cells). Insets are views of single channels of boxed regions. Asterisks mark the hub, and scale bars correspond to 10 μm. (I) The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of GFP signal quantification (n = 42 regions of germ cell debris in each genotype) is shown. Note the reduced GFP signal in the testis of drpr-null animals. Statistical significance was determined by a Mann-Whitney test, ****P ≤ 0.0001. (J) Schematic summarizing how cyst cells (green) induce phagoptosis of live germ cells (blue, left) resulting in lysosomal activity, DNA fragmentation, and PS exposure in germ cells (red, right).