Figure 3.
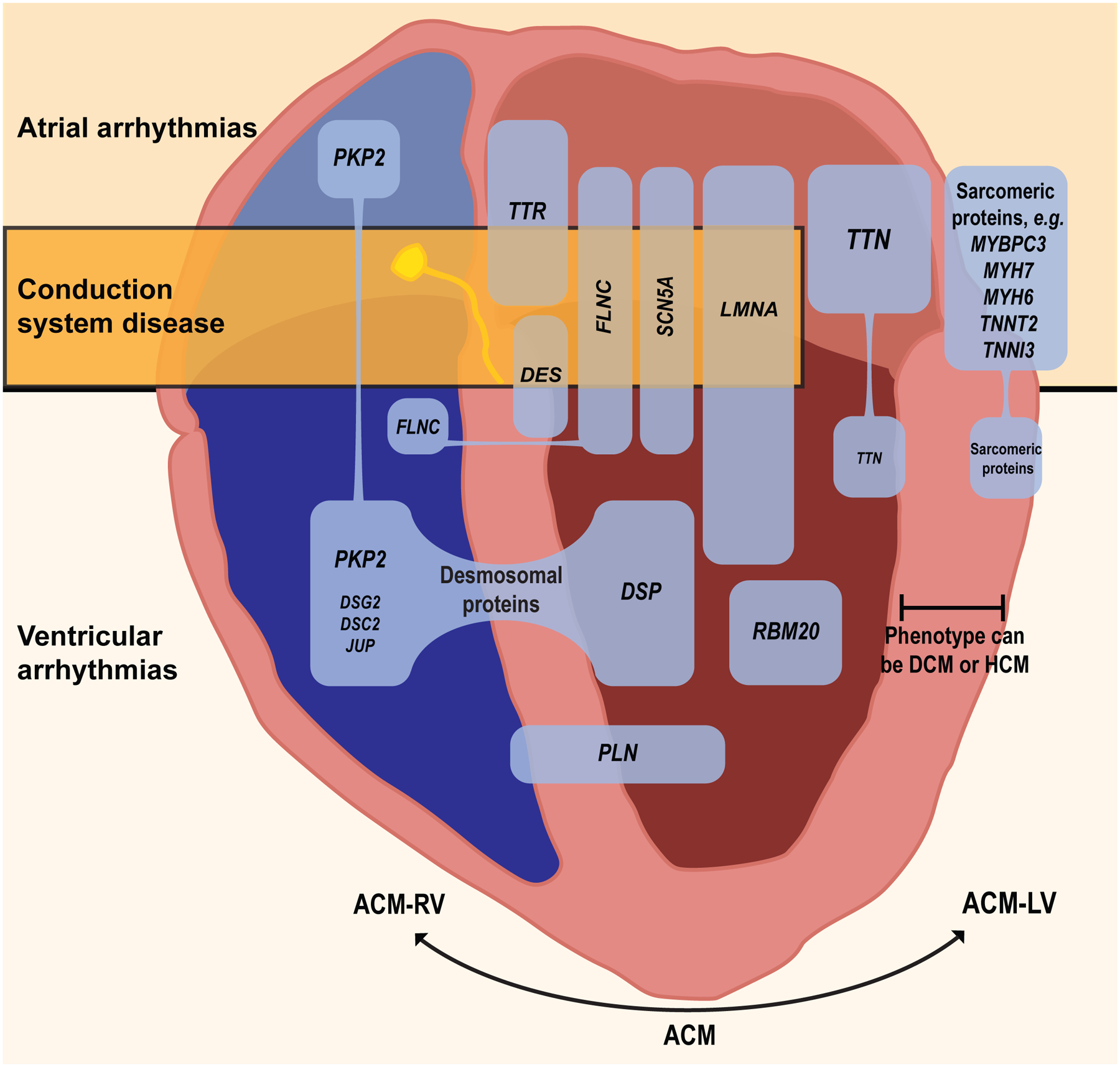
Examples of selected cardiomyopathy genes commonly associated with atrial or ventricular arrhythmias or conduction disease. The common genes coding for titin and the sarcomeric proteins are associated with a large number of variants, many of which are implicated in atrial fibrillation, but a minority of which are associated with ventricular arrhythmias, and conduction disease is rare. Variants recognized in less common genes such as LMNA and FLNC are more consistently associated with ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Variants in genes for desmosomal proteins, phospholamban, and filamin-C can be associated with both RV and LV involvement. ACM= general term for arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, ACM-RV = arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy with dominant RV involvement; ACM-LV= arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy with dominant LV involvement, DCM = dilated cardiomyopathy, HCM = hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. (Illustration credit: Ben Smith).
