Figure 1.
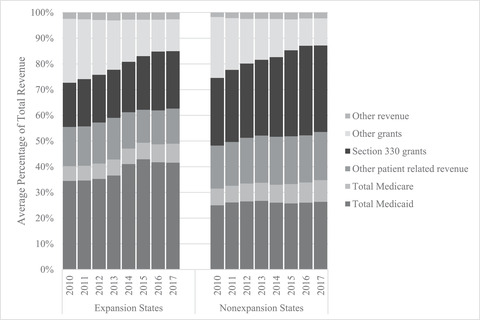
Payer Mix of FQHC Revenues by State Medicaid Expansion Status, 2010‐2017a
a State Medicaid expansion status is defined as a time‐invariant binary variable that captures whether an FQHC is located in a state that had expanded Medicaid eligibility by the end of 2014. There were 27 expansion states (MN, CT, DC, CA, WA, NJ, AZ, AR, CO, DE, HI, IL, IA, KY, MD, MA, NM, ND, NV, NY, OH, OR, RI, VT, WV, MI, NH) and 24 nonexpansion states (PA, IN, AK, MT, LA, ID, ME, NE, UT, VA, AL, FL, GA, KS, MS, MO, NC, OK, SC, SD, TN, TX, WI, WY). Sources of “other patient related revenue” include other public payers, private payers, and self‐pay. “Section 330 grants” include four types of funds under the Health Center Program authorized by Section 330 of the Public Health Service Act: for migrant health centers, for community health centers, for health care for the homeless, and for public housing primary care. “Other grants” include other BPHC grants, other federal grants, nonfederal grants, and contracts. “Other revenue” includes non‐patient‐related revenue not reported elsewhere. All revenues have been adjusted for inflation.
