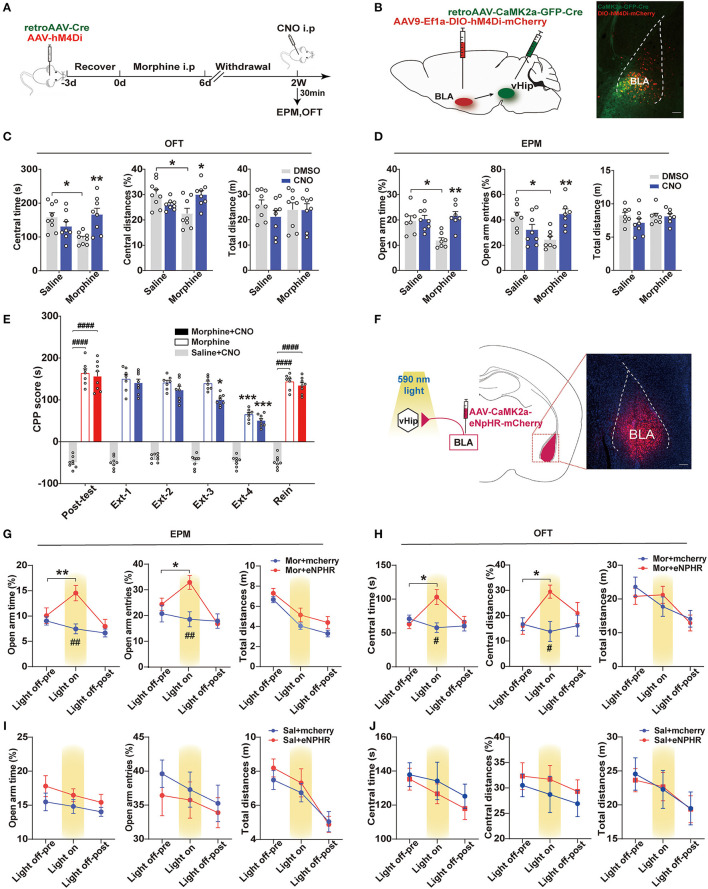
Figure 3.
BLA to vHip projections regulate anxiety-like behavior in morphine-withdrawn mice. (A–E) Chemogenetic experiment. (A) Workflow for the chemogenetic experiment. (B) Schematic (left) and representative image (right) of chemogenetic virus injection. Scale bar: 200 μm. (C) The Mor-A×CNO mice exhibited significantly increased central time and central distances in the OFT. (D) The Mor-A × CNO mice exhibited significantly increased open-arm times and entries in the EPM. (E) The hM4Di inhibition accelerated the decreased rate of morphine-paired preference in the Mor-A mice. (F–H) Optogenetic experiment. (F) Schematic of the virus injection site in the BLA and optical fiber implantation site in the vHip. (Right) Image of a coronal brain slice showing the expression of eNpHR-mCherry in the BLA. Scale bar: 200 μm. (G) Increased open-arm entries and time spent during the light-on epoch. (H) Increased time spent and distances traveled in the central area of the OFT during the eNpHR illumination epoch. The EPM (I) and OFT (J) tests of the saline + eNpHR group and the saline + mCherry group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. In the chemogenetic experiment, morphine CNO-treated mice were compared with morphine DMSO-treated mice. In the CPP results, *: comparison between the extinction group and the post-test group, #: comparison between the 2 indicated groups. In the optogenetic results, #: comparison between the Mor+mcherry and the Mor+eNPHR group during the light on epoch. n = 8–10/group.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ####P < 0.0001.