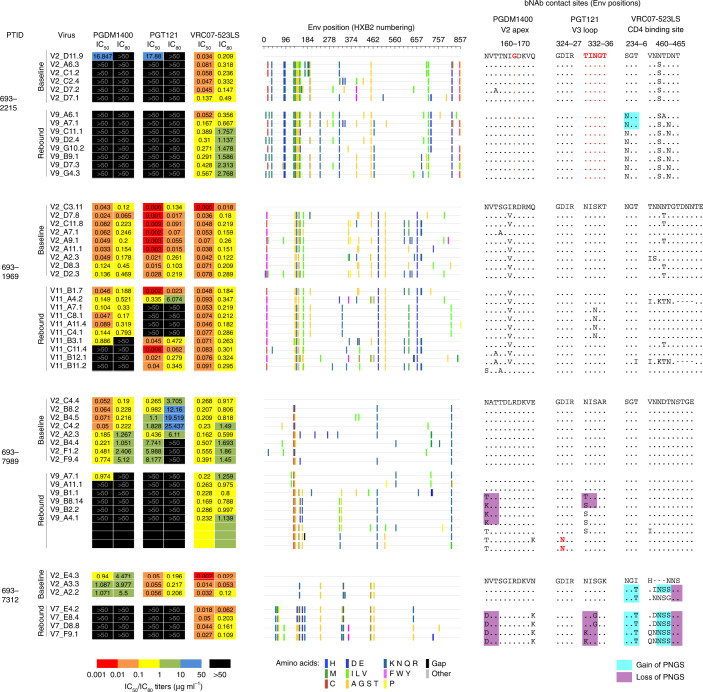
Fig. 3. Neutralization sensitivity to bNAbs and escape variants.
Left: For each participant, the pseudovirus IC50 and IC80 values (µg ml−1) for each bNAb are shown. Note: participant 693–7312 was treated with PGT121 and PGDM1400 dual therapy. Center: Highlighter plots showing amino acid Env mutations in participant viruses. The first baseline virus for each participant is treated as the reference sequence, and all amino acid mutations away from this reference Env are shown. Right: Env sequences for critical epitope sites for each of the bNAbs are shown. The first baseline Env for each participant is taken as the reference sequence, with dots for subsequent Envs indicating identity to the reference Env. Resistance mutations to each bNAb are highlighted in red. Gain or loss of PNGS as compared to the reference Env are highlighted with cyan or purple boxes, respectively. Note: loss of glycans 160 and 332 are associated with resistance to PGDM1400 and PGT121, respectively, whereas gain of glycan 234 and in hypervariable V5 loop are associated with resistance to VRC07-523LS. PTID, participant ID.