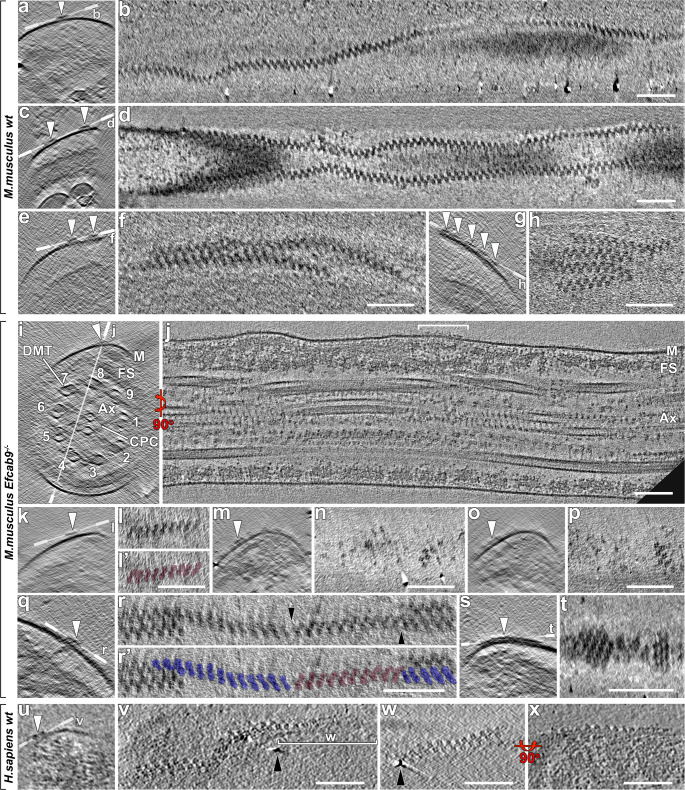
Fig. 2. In-cell structure of the native CatSper complexes in intact mammalian sperm flagella.
a–h Representative tomographic slices of the repeating CatSper channel complexes arranged in zigzag-rows along the longitudinal axis of wild type mouse sperm flagella shown as cross-sectional (a, c, e, g) and top views (b, d, f, h). The number of zigzag-rows (arrowheads) varied from a single row (a, b), two rows (c, d), merging rows (e, f), to up to five rows (g, h). i–j A representative principal piece region of a whole-cell (i.e., not cryo-FIB milled) Efcab9−/− mouse sperm flagellum (in non-capacitated state) viewed in cross-sectional (i) and longitudinal (j) tomographic slices. Labeled line in (i) indicates the position of the section shown in (j). Other labels: Ax axoneme, CPC central pair complex, DMT & 1-9 doublet microtubules, FS fibrous sheath, M membrane. k–t Representative tomographic slices from Efcab9−/− sperm showing fragmented and short CatSper complex clusters with altered orientation relative to the flagellar axis (cross section views: k, m, o, q, s; top views: l. l’, n, p, r, r’, t). Two distinct arrangements are pseudo-colored (backslash (\) blue and forward slash (/) pink) in (l’ and r’). Black arrowheads in (r) indicate the interruptions of the row. u–x Zigzag-arrangement of CatSper in a human sperm flagellum shown in cross-sectional (u), top (v, w) and side view (x). Black arrowheads in (v and w) indicate the same position between the two slices show at slightly different angles. Scale bars, 100 nm.