Figure 3.
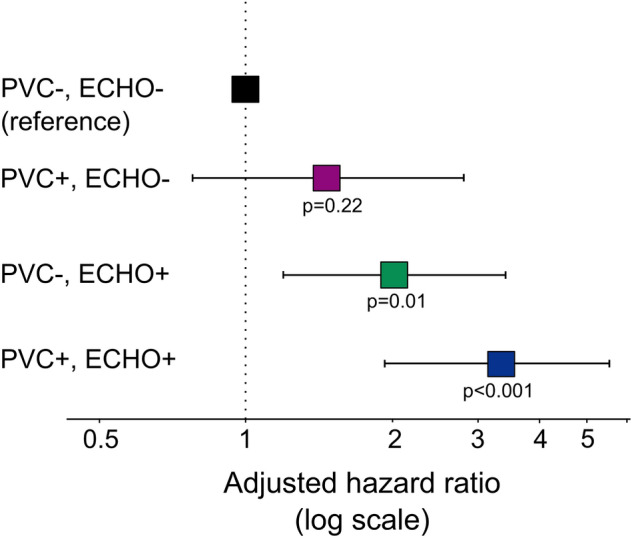
Forest plot showing hazard ratios for cardiovascular death with 95% confidence limits (adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, heart failure, ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, body mass index, peak workload, maximal heart rate, maximal systolic blood pressure, heart rate recovery, ST depression, and cardiovascular medications) based on combinations of presence/absence of PVC during recovery and echocardiographic abnormalities. ECHO− no significant abnormality on echocardiography, ECHO+ significant abnormality on echocardiography, PVC premature ventricular contractions, PVC− < 1 PVC/min during recovery, PVC+ ≥ 1 PVC/min during recovery. An echocardiographic abnormality was defined as either: reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, at least moderate valvular heart disease, left ventricular dilatation, increased left ventricular mass or increased filling pressures defined as E/e′ ≥ 15 and either dilated LA or increased RV–RA pressure gradient.
